class Subject[T] extends Observable[T] with Observer[T]
A Subject is an Observable and an Observer at the same time.
- Alphabetic
- By Inheritance
- Subject
- Observer
- Observable
- AnyRef
- Any
- Hide All
- Show All
- Public
- All
Instance Constructors
-
new
Subject(inner: SubjectFacade[T])
- Attributes
- protected
Type Members
-
class
WithFilter
[+A] extends AnyRef
- Definition Classes
- Observable
Value Members
-
final
def
!=(arg0: Any): Boolean
- Definition Classes
- AnyRef → Any
-
final
def
##(): Int
- Definition Classes
- AnyRef → Any
-
def
++[U >: T](other: Observable[U]): Observable[U]
Returns an Observable that first emits the items emitted by
this, and then the items emitted byother.Returns an Observable that first emits the items emitted by
this, and then the items emitted byother.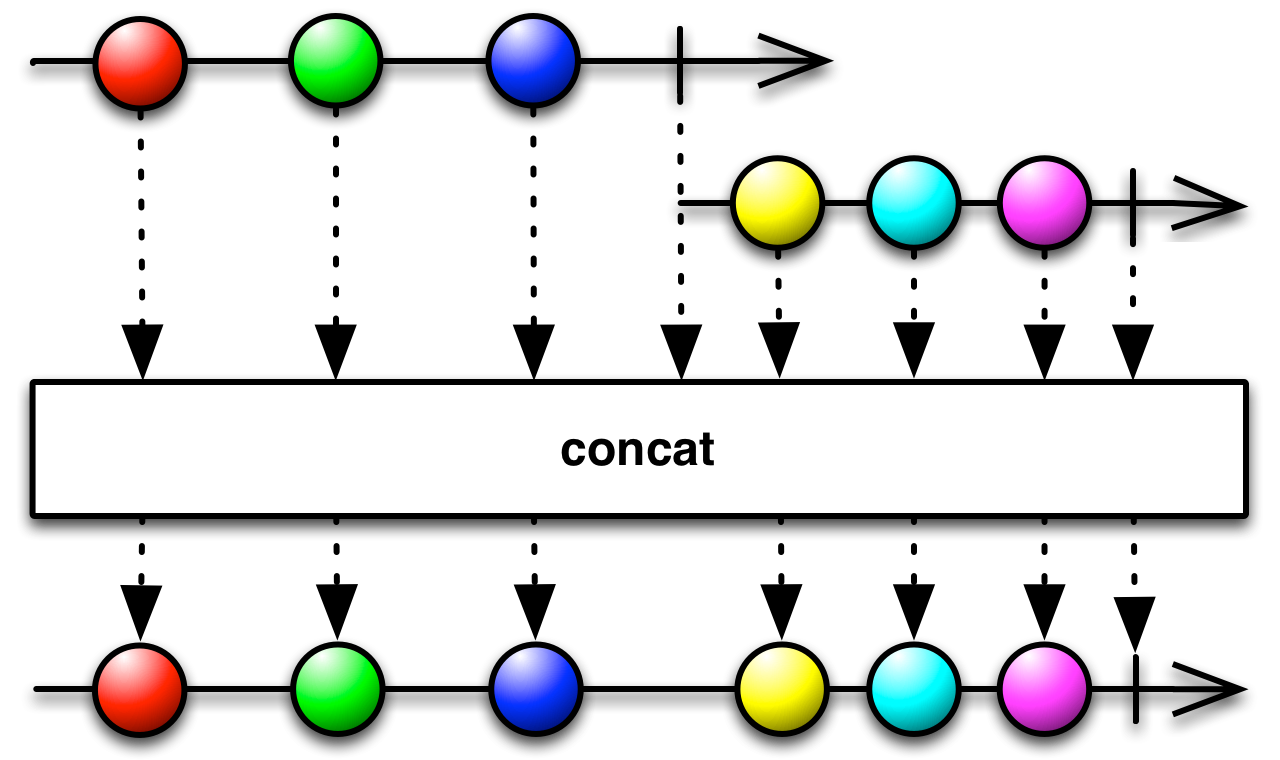
- other
an Observable to be appended
- returns
an Observable that emits items that are the result of combining the items emitted by this and that, one after the other
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
+:[U >: T](elem: U): Observable[U]
Returns an Observable that emits a specified item before it begins to emit items emitted by the source Observable.
Returns an Observable that emits a specified item before it begins to emit items emitted by the source Observable.
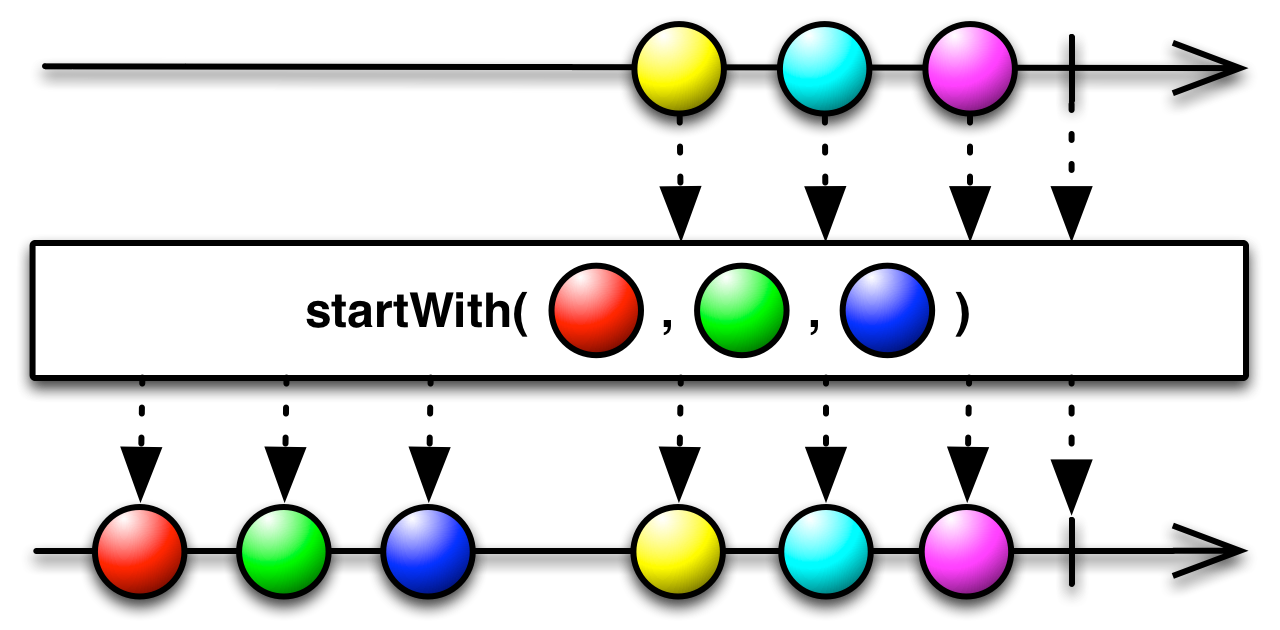
- elem
the item to emit
- returns
an Observable that emits the specified item before it begins to emit items emitted by the source Observable
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
final
def
==(arg0: Any): Boolean
- Definition Classes
- AnyRef → Any
-
def
apply(onNext: (T) ⇒ Unit): Subscription
Call this method to receive items from this observable.
Call this method to receive items from this observable.
- onNext
this function will be called whenever the Observable emits an item
- returns
a subscription.Subscription reference whose
unsubscribemethod can be called to stop receiving items before the Observable has finished sending them
- Definition Classes
- Observable
- See also
-
final
def
asInstanceOf[T0]: T0
- Definition Classes
- Any
- def asObservable(): Observable[T]
-
def
audit[I](durationSelector: (T) ⇒ Observable[I]): Observable[T]
Ignores source values for a duration determined by another Observable, then emits the most recent value from the source Observable, then repeats this process.
Ignores source values for a duration determined by another Observable, then emits the most recent value from the source Observable, then repeats this process.
It's like auditTime, but the silencing duration is determined by a second Observable.

auditis similar tothrottle, but emits the last value from the silenced time window, instead of the first value.auditemits the most recent value from the source Observable on the output Observable as soon as its internal timer becomes disabled, and ignores source values while the timer is enabled. Initially, the timer is disabled. As soon as the first source value arrives, the timer is enabled by calling thedurationSelectorfunction with the source value, which returns the "duration" Observable. When the duration Observable emits a value or completes, the timer is disabled, then the most recent source value is emitted on the output Observable, and this process repeats for the next source value.- durationSelector
A function that receives a value from the source Observable, for computing the silencing duration, returned as an Observable or a Promise.
- returns
{Observable[T]} An Observable that performs rate-limiting of emissions from the source Observable.
- Definition Classes
- Observable
Emit clicks at a rate of at most one click per second val result = clickStream.audit(ev => Observable.interval(1000)) result.subscribe(x => println(x))
Example: -
def
auditTime(delay: Int): Observable[T]
Ignores source values for
durationmilliseconds, then emits the most recent value from the source Observable, then repeats this process.Ignores source values for
durationmilliseconds, then emits the most recent value from the source Observable, then repeats this process.When it sees a source values, it ignores that plus the next ones for `duration` milliseconds, and then it emits the most recent value from the source.

auditTimeis similar tothrottleTime, but emits the last value from the silenced time window, instead of the first value.auditTimeemits the most recent value from the source Observable on the output Observable as soon as its internal timer becomes disabled, and ignores source values while the timer is enabled. Initially, the timer is disabled. As soon as the first source value arrives, the timer is enabled. Afterdurationmilliseconds (or the time unit determined internally by the optionalscheduler) has passed, the timer is disabled, then the most recent source value is emitted on the output Observable, and this process repeats for the next source value. Optionally takes a Scheduler for managing timers.- delay
Time to wait before emitting the most recent source value, measured in milliseconds or the time unit determined internally by the optional
scheduler.- returns
An Observable that performs rate-limiting of emissions from the source Observable.
- Definition Classes
- Observable
Emit clicks at a rate of at most one click per second val clicks = Observable.fromEvent(document, "click") val result = clicks.auditTime(1000) result.subscribe(x => println(x))
Example: -
def
auditTime(delay: Int, scheduler: Scheduler): Observable[T]
Ignores source values for
durationmilliseconds, then emits the most recent value from the source Observable, then repeats this process.Ignores source values for
durationmilliseconds, then emits the most recent value from the source Observable, then repeats this process.When it sees a source values, it ignores that plus the next ones for `duration` milliseconds, and then it emits the most recent value from the source.

auditTimeis similar tothrottleTime, but emits the last value from the silenced time window, instead of the first value.auditTimeemits the most recent value from the source Observable on the output Observable as soon as its internal timer becomes disabled, and ignores source values while the timer is enabled. Initially, the timer is disabled. As soon as the first source value arrives, the timer is enabled. Afterdurationmilliseconds (or the time unit determined internally by the optionalscheduler) has passed, the timer is disabled, then the most recent source value is emitted on the output Observable, and this process repeats for the next source value. Optionally takes a Scheduler for managing timers.- delay
Time to wait before emitting the most recent source value, measured in milliseconds or the time unit determined internally by the optional
scheduler.- scheduler
The Scheduler to use for managing the timers that handle the rate-limiting behavior.
- returns
An Observable that performs rate-limiting of emissions from the source Observable.
- Definition Classes
- Observable
Emit clicks at a rate of at most one click per second val clicks = Observable.fromEvent(document, "click") val result = clicks.auditTime(1000) result.subscribe(x => println(x))
Example: -
def
buffer[T2](closingNotifier: Observable[T2]): Observable[List[T]]
Creates an Observable which produces buffers of collected values.
Creates an Observable which produces buffers of collected values.
Buffers the incoming Observable values until the given
closingNotifierObservable emits a value, at which point it emits the buffer on the output Observable and starts a new buffer internally, awaiting the next timeclosingNotifieremits.
- closingNotifier
An Observable that signals the buffer to be emitted on the output Observable.
- returns
An Observable of buffers, which are arrays of values.
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
bufferCount(count: Int): Observable[List[T]]
Creates an Observable which produces buffers of collected values.
Creates an Observable which produces buffers of collected values.
This Observable produces connected non-overlapping buffers, each containing
countelements. When the source Observable completes or encounters an error, the current buffer is emitted, and the event is propagated.
- count
The maximum size of each buffer before it should be emitted.
- returns
An rxscalajs.Observable which produces connected non-overlapping buffers containing at most
countproduced values.
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
bufferCount(count: Int, skip: Int): Observable[List[T]]
Creates an Observable which produces windows of collected values.
Creates an Observable which produces windows of collected values. This Observable produces windows every
skipvalues, each containingcountelements. When the source Observable completes or encounters an error, the current window is emitted and the event is propagated.
- count
The maximum size of each window before it should be emitted.
- skip
How many produced values need to be skipped before starting a new window. Note that when
skipandcountare equal that this is the same operation aswindow(int).- returns
An rxscalajs.Observable which produces windows every
skipvalues containing at mostbufferSizeproduced values.
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
bufferTime(bufferTimeSpan: FiniteDuration): Observable[List[T]]
Creates an Observable which produces buffers of collected values.
Creates an Observable which produces buffers of collected values.
This Observable produces connected non-overlapping buffers, each of a fixed duration specified by the
timespanargument. When the source Observable completes or encounters an error, the current buffer is emitted and the event is propagated.- bufferTimeSpan
The period of time each buffer is collecting values before it should be emitted, and replaced with a new buffer.
- returns
An rxscalajs.Observable which produces connected non-overlapping buffers with a fixed duration.
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
bufferTime(bufferTimeSpan: Int, bufferCreationInterval: Int): Observable[List[T]]
Creates an Observable which produces buffers of collected values.
Creates an Observable which produces buffers of collected values. This Observable starts a new buffer periodically, which is determined by the
timeshiftargument. Each buffer is emitted after a fixed timespan specified by thetimespanargument. When the source Observable completes or encounters an error, the current buffer is emitted and the event is propagated.- bufferTimeSpan
The period of time each buffer is collecting values before it should be emitted.
- bufferCreationInterval
The period of time after which a new buffer will be created.
- returns
An rxscalajs.Observable which produces new buffers periodically, and these are emitted after a fixed timespan has elapsed.
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
bufferTime(bufferTimeSpan: FiniteDuration, bufferCreationInterval: FiniteDuration): Observable[List[T]]
Creates an Observable which produces buffers of collected values.
Creates an Observable which produces buffers of collected values. This Observable starts a new buffer periodically, which is determined by the
timeshiftargument. Each buffer is emitted after a fixed timespan specified by thetimespanargument. When the source Observable completes or encounters an error, the current buffer is emitted and the event is propagated.- bufferTimeSpan
The period of time each buffer is collecting values before it should be emitted.
- bufferCreationInterval
The period of time after which a new buffer will be created.
- returns
An rxscalajs.Observable which produces new buffers periodically, and these are emitted after a fixed timespan has elapsed.
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
bufferTime(bufferTimeSpan: FiniteDuration, bufferCreationInterval: FiniteDuration, scheduler: Scheduler): Observable[List[T]]
Creates an Observable which produces buffers of collected values.
Creates an Observable which produces buffers of collected values. This Observable starts a new buffer periodically, which is determined by the
timeshiftargument. Each buffer is emitted after a fixed timespan specified by thetimespanargument. When the source Observable completes or encounters an error, the current buffer is emitted and the event is propagated.- bufferTimeSpan
The period of time each buffer is collecting values before it should be emitted.
- bufferCreationInterval
The period of time after which a new buffer will be created.
- scheduler
The rxscalajs.Scheduler to use when determining the end and start of a buffer.
- returns
An rxscalajs.Observable which produces new buffers periodically, and these are emitted after a fixed timespan has elapsed.
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
bufferToggle[T2, O](openings: Observable[O])(closingSelector: (O) ⇒ Observable[T2]): Observable[List[T]]
Buffers the source Observable values starting from an emission from
openingsand ending when the output ofclosingSelectoremits.Buffers the source Observable values starting from an emission from
openingsand ending when the output ofclosingSelectoremits.Collects values from the past as an array. Starts collecting only when `opening` emits, and calls the `closingSelector` function to get an Observable that tells when to close the buffer.

Buffers values from the source by opening the buffer via signals from an Observable provided to
openings, and closing and sending the buffers when a Subscribable or Promise returned by theclosingSelectorfunction emits.- openings
An Observable or Promise of notifications to start new buffers.
- closingSelector
A function that takes the value emitted by the
openingsobservable and returns a Subscribable or Promise, which, when it emits, signals that the associated buffer should be emitted and cleared.- returns
An observable of arrays of buffered values.
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
bufferWhen[T2](closingSelector: () ⇒ Observable[T2]): Observable[List[T]]
Buffers the source Observable values, using a factory function of closing Observables to determine when to close, emit, and reset the buffer.
Buffers the source Observable values, using a factory function of closing Observables to determine when to close, emit, and reset the buffer.
Collects values from the past as an array. When it starts collecting values, it calls a function that returns an Observable that tells when to close the buffer and restart collecting.

Opens a buffer immediately, then closes the buffer when the observable returned by calling
closingSelectorfunction emits a value. When it closes the buffer, it immediately opens a new buffer and repeats the process.- closingSelector
A function that takes no arguments and returns an Observable that signals buffer closure.
- returns
An observable of arrays of buffered values.
- Definition Classes
- Observable
Emit an array of the last clicks every [1-5] random seconds val clicks = Observable.fromEvent(document, "click") val buffered = clicks.bufferWhen(() => Observable.interval(1000 + Math.random() * 4000) ) buffered.subscribe(x => println(x))
Example: -
def
catchError[U >: T](resumeFunction: (Any) ⇒ Observable[U]): Observable[U]
Continues an observable sequence that is terminated by an exception with the next observable sequence.
Continues an observable sequence that is terminated by an exception with the next observable sequence.

- resumeFunction
Exception handler function that returns an observable sequence given the error that occurred in the first sequence
- returns
An observable sequence containing the first sequence's elements, followed by the elements of the handler sequence in case an exception occurred.
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
clone(): AnyRef
- Attributes
- protected[java.lang]
- Definition Classes
- AnyRef
- Annotations
- @throws( ... )
-
def
collect[B](partialProject: PartialFunction[T, B]): Observable[B]
Scala API Same as map, but with PartialFunction, where observable emits elements only for defined values
Scala API Same as map, but with PartialFunction, where observable emits elements only for defined values
- partialProject
Partial function that will be applied to elements for which it is defined
- returns
An observable sequence containing the first sequence elements projected by
partialProjectfor which it was defined.
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
combineAll[U, R](project: (Array[U]) ⇒ R)(implicit evidence: <:<[Observable[T], Observable[Observable[U]]]): Observable[R]
Converts a higher-order Observable into a first-order Observable by waiting for the outer Observable to complete, then applying
combineLatest.Converts a higher-order Observable into a first-order Observable by waiting for the outer Observable to complete, then applying
combineLatest.Flattens an Observable-of-Observables by applying `[[combineLatest]]` when the Observable-of-Observables completes.

Takes an Observable of Observables, and collects all Observables from it. Once the outer Observable completes, it subscribes to all collected Observables and combines their values using the
combineLateststrategy, such that: - Every time an inner Observable emits, the output Observable emits. - When the returned observable emits, it emits all of the latest values by:- If a
projectfunction is provided, it is called with each recent value from each inner Observable in whatever order they arrived, and the result of theprojectfunction is what is emitted by the output Observable. - If there is no
projectfunction, an array of all of the most recent values is emitted by the output Observable.
- project
An optional function to map the most recent values from each inner Observable into a new result. Takes each of the most recent values from each collected inner Observable as arguments, in order.
- returns
{Observable} An Observable of projected results or arrays of recent values.
- Definition Classes
- Observable
Map two click events to a finite interval Observable, then apply combineAll var clicks = Observable.fromEvent(document, "click") var higherOrder = clicks.map(ev => Observable.interval(Math.random()*2000).take(3) ).take(2) var result = higherOrder.combineAll() result.subscribe(x => println(x))
Example: - If a
-
def
combineAll[U](implicit evidence: <:<[Observable[T], Observable[Observable[U]]]): Observable[Seq[U]]
Converts a higher-order Observable into a first-order Observable by waiting for the outer Observable to complete, then applying
combineLatest.Converts a higher-order Observable into a first-order Observable by waiting for the outer Observable to complete, then applying
combineLatest.Flattens an Observable-of-Observables by applying `[[combineLatest]]` when the Observable-of-Observables completes.

Takes an Observable of Observables, and collects all Observables from it. Once the outer Observable completes, it subscribes to all collected Observables and combines their values using the
combineLateststrategy, such that: - Every time an inner Observable emits, the output Observable emits. - When the returned observable emits, it emits all of the latest values by:- If a
projectfunction is provided, it is called with each recent value from each inner Observable in whatever order they arrived, and the result of theprojectfunction is what is emitted by the output Observable. - If there is no
projectfunction, an array of all of the most recent values is emitted by the output Observable.
- returns
{Observable} An Observable of projected results or arrays of recent values.
- Definition Classes
- Observable
Map two click events to a finite interval Observable, then apply combineAll var clicks = Observable.fromEvent(document, "click") var higherOrder = clicks.map(ev => Observable.interval(Math.random()*2000).take(3) ).take(2) var result = higherOrder.combineAll result.subscribe(x => println(x))
Example: - If a
-
def
combineLatest[U, V, W](first: Observable[U], second: Observable[V], third: Observable[W]): Observable[(T, U, V, W)]
Combines four observables, emitting a tuple of the latest values of each of the source observables each time an event is received from one of the source observables.
Combines four observables, emitting a tuple of the latest values of each of the source observables each time an event is received from one of the source observables.

- first
an Observable to be combined
- second
an Observable to be combined
- third
an Observable to be combined
- returns
An Observable that combines the source Observables
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
combineLatest[U, V](first: Observable[U], second: Observable[V]): Observable[(T, U, V)]
Combines four observables, emitting a tuple of the latest values of each of the source observables each time an event is received from one of the source observables.
Combines four observables, emitting a tuple of the latest values of each of the source observables each time an event is received from one of the source observables.

- first
an Observable to be combined
- second
an Observable to be combined
- returns
An Observable that combines the source Observables
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
combineLatest[U](that: Observable[U]): Observable[(T, U)]
Combines two observables, emitting a combination of the latest values of each of the source observables each time an event is received from one of the source observables.
Combines two observables, emitting a combination of the latest values of each of the source observables each time an event is received from one of the source observables.

- that
The second source observable.
- returns
An Observable that combines the source Observables
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
combineLatestWith[U, V, W, R](first: Observable[U], second: Observable[V], third: Observable[W])(selector: (T, U, V, W) ⇒ R): Observable[R]
Combines four observables, emitting some type
Rspecified in the functionselector, each time an event is received from one of the source observables, where the aggregation is defined by the given function.Combines four observables, emitting some type
Rspecified in the functionselector, each time an event is received from one of the source observables, where the aggregation is defined by the given function.
- first
an Observable to be combined
- second
an Observable to be combined
- third
an Observable to be combined
- selector
The function that is used combine the emissions of the four observables.
- returns
An Observable that combines the source Observables according to the function selector.
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
combineLatestWith[U, V, R](first: Observable[U], second: Observable[V])(selector: (T, U, V) ⇒ R): Observable[R]
Combines three observables, emitting some type
Rspecified in the functionselector, each time an event is received from one of the source observables, where the aggregation is defined by the given function.Combines three observables, emitting some type
Rspecified in the functionselector, each time an event is received from one of the source observables, where the aggregation is defined by the given function.
- first
an Observable to be combined
- second
an Observable to be combined
- selector
The function that is used combine the emissions of the three observables.
- returns
An Observable that combines the source Observables according to the function selector.
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
combineLatestWith[U, R](that: Observable[U])(selector: (T, U) ⇒ R): Observable[R]
Combines two observables, emitting some type
Rspecified in the functionselector, each time an event is received from one of the source observables, where the aggregation is defined by the given function.Combines two observables, emitting some type
Rspecified in the functionselector, each time an event is received from one of the source observables, where the aggregation is defined by the given function.
- that
The second source observable.
- selector
The function that is used combine the emissions of the two observables.
- returns
An Observable that combines the source Observables according to the function selector.
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
complete(): Unit
Notifies the Observer that the rxscalajs.Observable has finished sending push-based notifications.
Notifies the Observer that the rxscalajs.Observable has finished sending push-based notifications.
The rxscalajs.Observable will not call this method if it calls
error. -
def
concat[U >: T](other: Observable[U]): Observable[U]
Returns an Observable that first emits the items emitted by
this, and then the items emitted byother.Returns an Observable that first emits the items emitted by
this, and then the items emitted byother.
- other
an Observable to be appended
- returns
an Observable that emits items that are the result of combining the items emitted by this and that, one after the other
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
concatAll[U](implicit evidence: <:<[Observable[T], Observable[Observable[U]]]): Observable[U]
Returns an Observable that emits the items emitted by several Observables, one after the other.
Returns an Observable that emits the items emitted by several Observables, one after the other.

This operation is only available if
thisis of typeObservable[Observable[U]]for someU, otherwise you'll get a compilation error.- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
concatMap[R](project: (T) ⇒ Observable[R]): Observable[R]
Returns a new Observable that emits items resulting from applying a function that you supply to each item emitted by the source Observable, where that function returns an Observable, and then emitting the items that result from concatinating those resulting Observables.
Returns a new Observable that emits items resulting from applying a function that you supply to each item emitted by the source Observable, where that function returns an Observable, and then emitting the items that result from concatinating those resulting Observables.
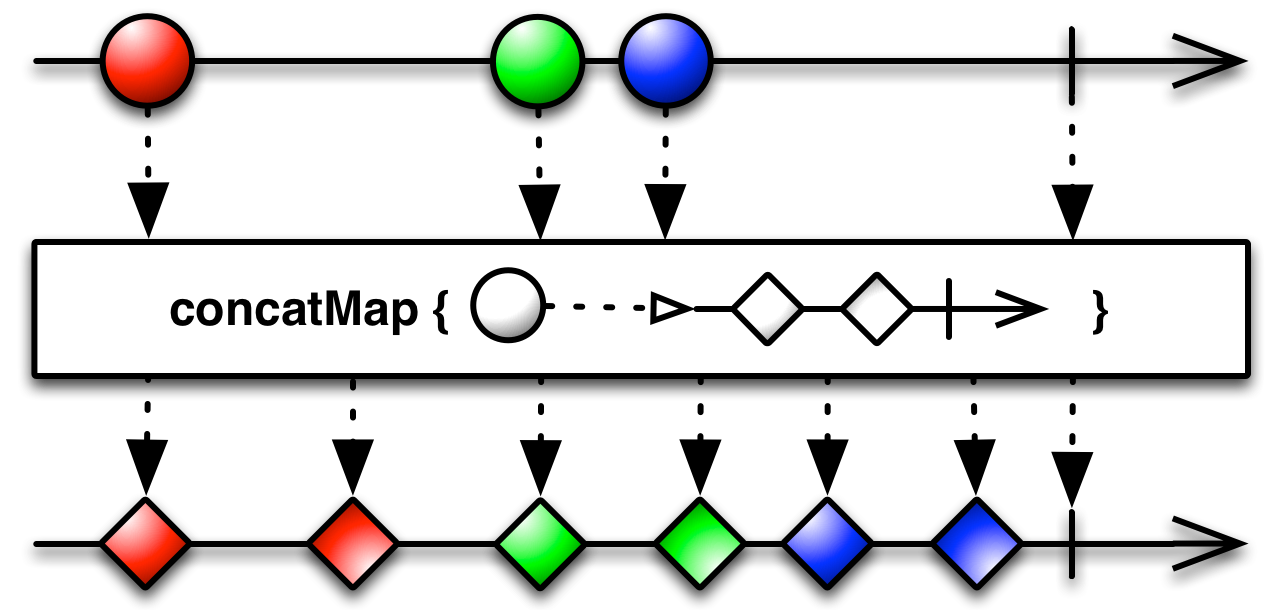
- project
a function that, when applied to an item emitted by the source Observable, returns an Observable
- returns
an Observable that emits the result of applying the transformation function to each item emitted by the source Observable and concatinating the Observables obtained from this transformation
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
concatMapTo[R](innerObservable: Observable[R]): Observable[R]
Projects each source value to the same Observable which is merged multiple times in a serialized fashion on the output Observable.
Projects each source value to the same Observable which is merged multiple times in a serialized fashion on the output Observable.

- innerObservable
a function that, when applied to an item emitted by the source Observable, returns an Observable
- returns
an Observable that emits the result of applying the transformation function to each item emitted by the source Observable and concatinating the Observables obtained from this transformation
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
count: Observable[Int]
Return an Observable which emits the number of elements in the source.
Return an Observable which emits the number of elements in the source.
- returns
an Observable which emits the number of elements in the source.
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
count(predicate: (T, Int, Observable[T]) ⇒ Boolean): Observable[Int]
Return an Observable which emits the number of elements in the source Observable which satisfy a predicate.
Return an Observable which emits the number of elements in the source Observable which satisfy a predicate.
- predicate
the predicate used to test elements.
- returns
an Observable which emits the number of elements in the source Observable which satisfy a predicate.
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
debounce(debounceSelector: (T) ⇒ Observable[Int]): Observable[T]
Return an Observable that mirrors the source Observable, except that it drops items emitted by the source Observable that are followed by another item within a computed debounce duration.
Return an Observable that mirrors the source Observable, except that it drops items emitted by the source Observable that are followed by another item within a computed debounce duration.
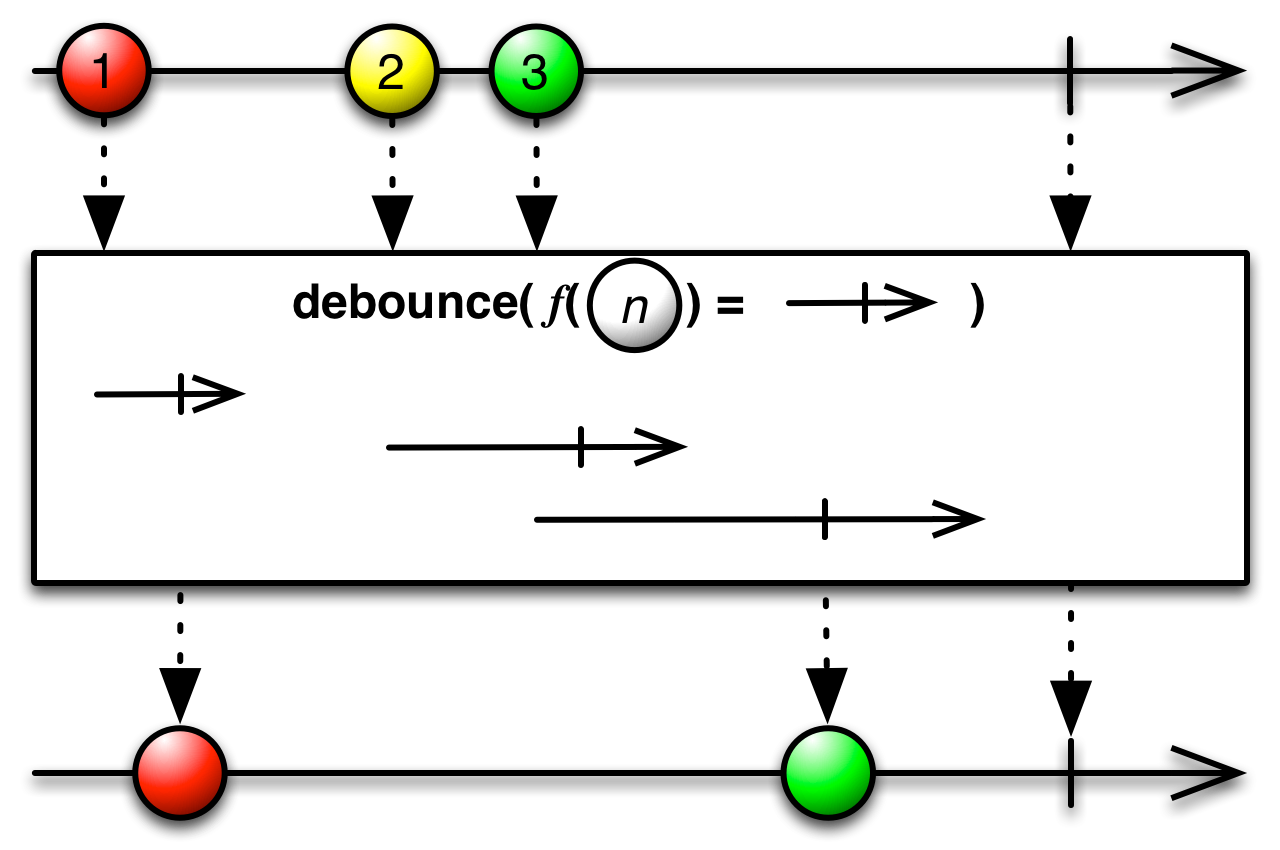
- debounceSelector
function to retrieve a sequence that indicates the throttle duration for each item
- returns
an Observable that omits items emitted by the source Observable that are followed by another item within a computed debounce duration
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
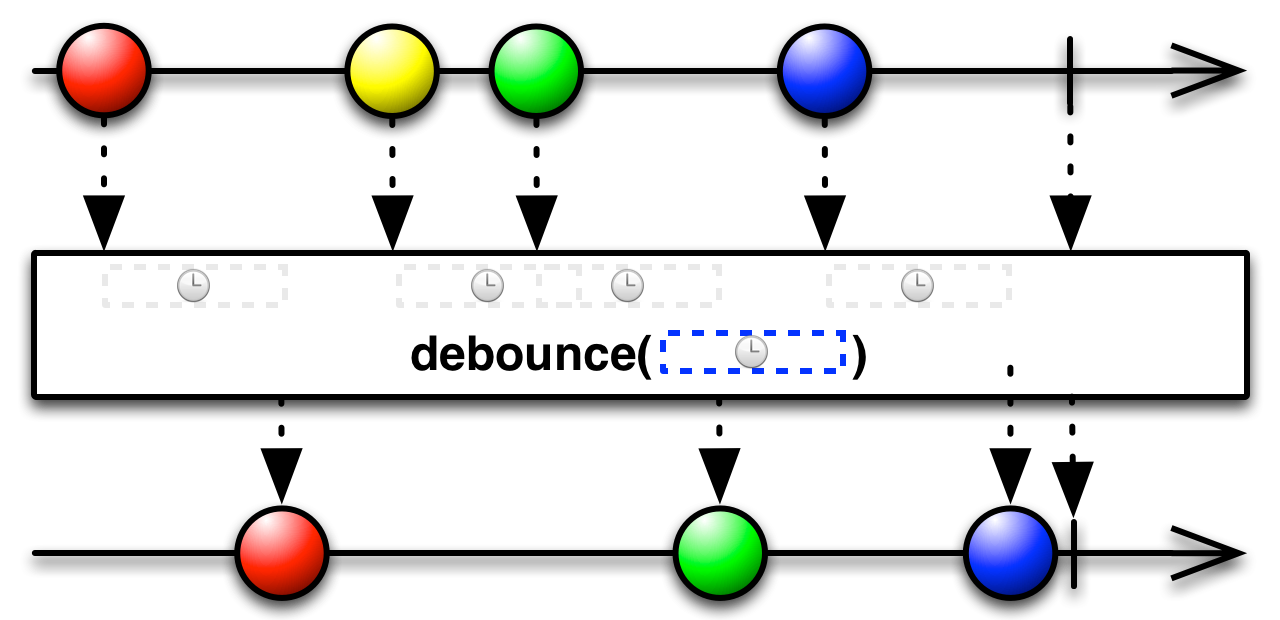
debounceTime(timeout: Int): Observable[T]
Debounces by dropping all values that are followed by newer values before the timeout value expires.
Debounces by dropping all values that are followed by newer values before the timeout value expires. The timer resets on each
onNextcall.NOTE: If events keep firing faster than the timeout then no data will be emitted.
Information on debounce vs throttle: - http://drupalmotion.com/article/debounce-and-throttle-visual-explanation - http://unscriptable.com/2009/03/20/debouncing-javascript-methods/ - http://www.illyriad.co.uk/blog/index.php/2011/09/javascript-dont-spam-your-server-debounce-and-throttle/
- timeout
The time each value has to be 'the most recent' of the Observable to ensure that it's not dropped.
- returns
An Observable which filters out values which are too quickly followed up with newer values.
- Definition Classes
- Observable
- See also
Observable.throttleWithTimeout
-
def
debounceTime(timeout: FiniteDuration): Observable[T]
Debounces by dropping all values that are followed by newer values before the timeout value expires.
Debounces by dropping all values that are followed by newer values before the timeout value expires. The timer resets on each
onNextcall.NOTE: If events keep firing faster than the timeout then no data will be emitted.

Information on debounce vs throttle: - http://drupalmotion.com/article/debounce-and-throttle-visual-explanation - http://unscriptable.com/2009/03/20/debouncing-javascript-methods/ - http://www.illyriad.co.uk/blog/index.php/2011/09/javascript-dont-spam-your-server-debounce-and-throttle/
- timeout
The time each value has to be 'the most recent' of the Observable to ensure that it's not dropped.
- returns
An Observable which filters out values which are too quickly followed up with newer values.
- Definition Classes
- Observable
- See also
Observable.throttleWithTimeout
-
def
defaultIfEmpty[R](defaultValue: ⇒ R): Observable[R]
Returns an Observable that emits the items emitted by the source Observable or a specified default item if the source Observable is empty.
Returns an Observable that emits the items emitted by the source Observable or a specified default item if the source Observable is empty.

- defaultValue
the item to emit if the source Observable emits no items. This is a by-name parameter, so it is only evaluated if the source Observable doesn't emit anything.
- returns
an Observable that emits either the specified default item if the source Observable emits no items, or the items emitted by the source Observable
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
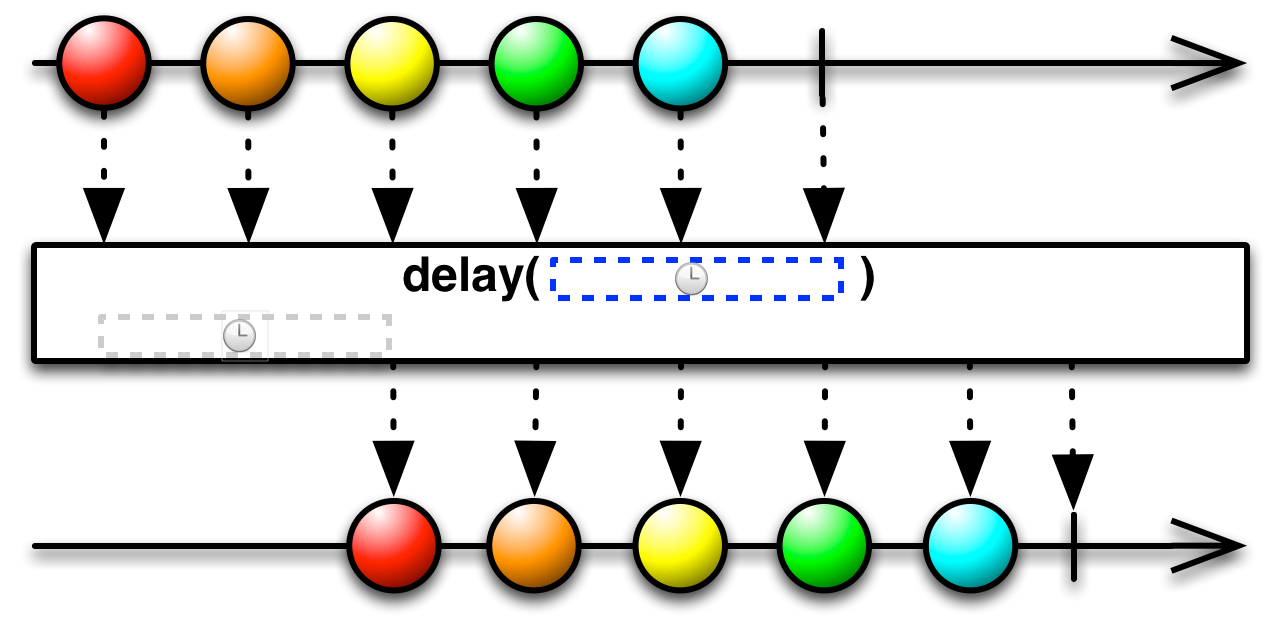
delay(delay: Int): Observable[T]
Returns an Observable that emits the items emitted by the source Observable shifted forward in time by a specified delay.
Returns an Observable that emits the items emitted by the source Observable shifted forward in time by a specified delay. Error notifications from the source Observable are not delayed.
- delay
the delay to shift the source by
- returns
the source Observable shifted in time by the specified delay
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
delay(delay: FiniteDuration): Observable[T]
Returns an Observable that emits the items emitted by the source Observable shifted forward in time by a specified delay.
Returns an Observable that emits the items emitted by the source Observable shifted forward in time by a specified delay. Error notifications from the source Observable are not delayed.

- delay
the delay to shift the source by
- returns
the source Observable shifted in time by the specified delay
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
delayWhen[U, I](delayDurationSelector: (T) ⇒ Observable[U]): Observable[T]
Returns an Observable that delays the emissions of the source Observable via another Observable on a per-item basis.
Returns an Observable that delays the emissions of the source Observable via another Observable on a per-item basis.
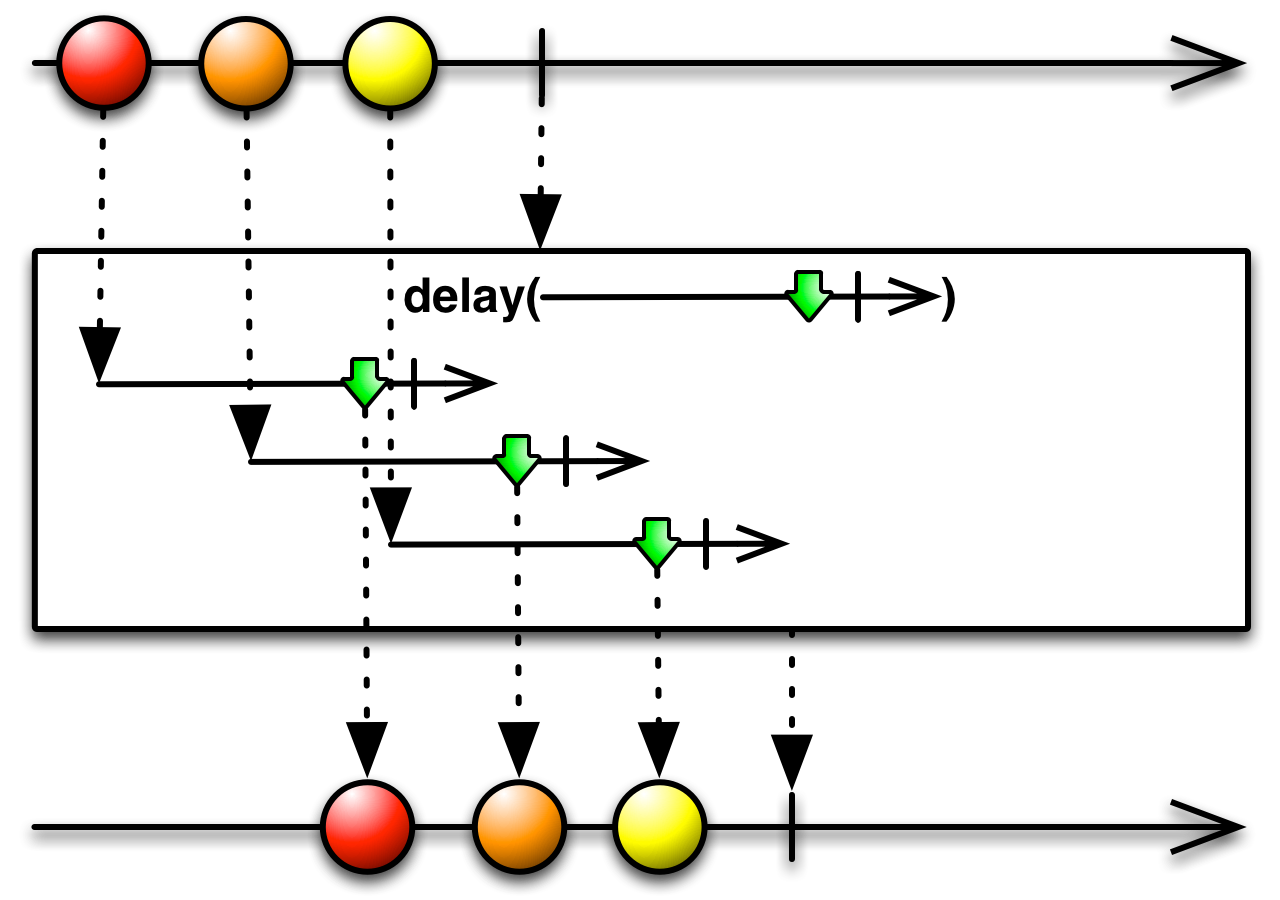
Note: the resulting Observable will immediately propagate any
onErrornotification from the source Observable.- delayDurationSelector
a function that returns an Observable for each item emitted by the source Observable, which is then used to delay the emission of that item by the resulting Observable until the Observable returned from
itemDelayemits an item- returns
an Observable that delays the emissions of the source Observable via another Observable on a per-item basis
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
delayWhen[U, I](delayDurationSelector: (T) ⇒ Observable[U], subscriptionDelay: Observable[I]): Observable[T]
Returns an Observable that delays the emissions of the source Observable via another Observable on a per-item basis.
Returns an Observable that delays the emissions of the source Observable via another Observable on a per-item basis.

Note: the resulting Observable will immediately propagate any
onErrornotification from the source Observable.- delayDurationSelector
a function that returns an Observable for each item emitted by the source Observable, which is then used to delay the emission of that item by the resulting Observable until the Observable returned from
itemDelayemits an item- subscriptionDelay
a function that returns an Observable that triggers the subscription to the source Observable once it emits any item
- returns
an Observable that delays the emissions of the source Observable via another Observable on a per-item basis
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
dematerialize[U]: Observable[U]
[use case] Returns an Observable that reverses the effect of rxscalajs.Observable.materialize by transforming the rxscalajs.Notification objects emitted by the source Observable into the items or notifications they represent.
[use case]Returns an Observable that reverses the effect of rxscalajs.Observable.materialize by transforming the rxscalajs.Notification objects emitted by the source Observable into the items or notifications they represent.
This operation is only available if
thisis of typeObservable[Notification[U]]for someU, otherwise you will get a compilation error.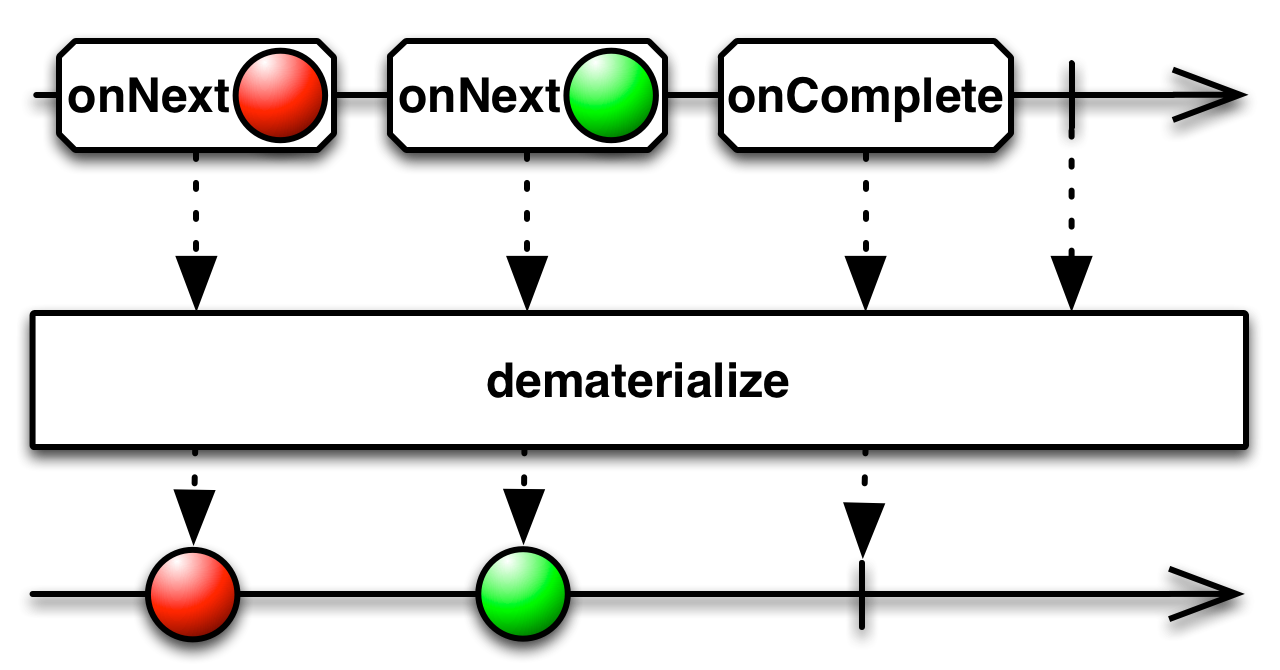
- returns
an Observable that emits the items and notifications embedded in the rxscalajs.Notification objects emitted by the source Observable
- Definition Classes
- Observable
Full Signaturedef dematerialize[T2]: Observable[T2]
-
def
distinct[T2]: Observable[T]
Returns an Observable that forwards all items emitted from the source Observable that are distinct according to a key selector function.
Returns an Observable that forwards all items emitted from the source Observable that are distinct according to a key selector function.

- returns
an Observable of distinct items
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
distinct[K](keySelector: (T) ⇒ K): Observable[T]
Returns an Observable that forwards all items emitted from the source Observable that are distinct according to a key selector function.
Returns an Observable that forwards all items emitted from the source Observable that are distinct according to a key selector function.

- returns
an Observable of distinct items
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
distinct[T2](flushes: Observable[T2]): Observable[T]
Returns an Observable that forwards all items emitted from the source Observable that are distinct according to a key selector function.
Returns an Observable that forwards all items emitted from the source Observable that are distinct according to a key selector function.

- flushes
Observable for flushing the internal HashSet of the operator.
- returns
an Observable of distinct items
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
distinct[K, T2](keySelector: (T) ⇒ K, flushes: Observable[T2]): Observable[T]
Returns an Observable that forwards all items emitted from the source Observable that are distinct according to a key selector function.
Returns an Observable that forwards all items emitted from the source Observable that are distinct according to a key selector function.

- keySelector
function to select which value you want to check as distinct.
- flushes
Observable for flushing the internal HashSet of the operator.
- returns
an Observable of distinct items
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
distinctUntilChanged: Observable[T]
Returns an Observable that forwards all items emitted from the source Observable that are sequentially distinct according to a key selector function.
Returns an Observable that forwards all items emitted from the source Observable that are sequentially distinct according to a key selector function.

- returns
an Observable of sequentially distinct items
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
distinctUntilChanged(compare: (T, T) ⇒ Boolean): Observable[T]
Returns an Observable that forwards all items emitted from the source Observable that are sequentially distinct according to a key selector function.
Returns an Observable that forwards all items emitted from the source Observable that are sequentially distinct according to a key selector function.

- compare
a function that compares the two items
- returns
an Observable of sequentially distinct items
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
distinctUntilChanged[K](compare: (K, K) ⇒ Boolean, keySelector: (T) ⇒ K): Observable[T]
Returns an Observable that forwards all items emitted from the source Observable that are sequentially distinct according to a key selector function.
Returns an Observable that forwards all items emitted from the source Observable that are sequentially distinct according to a key selector function.

- compare
a function that compares the two items
- keySelector
a function that projects an emitted item to a key value which is used for deciding whether an item is sequentially distinct from another one or not
- returns
an Observable of sequentially distinct items
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
drop(total: Int): Observable[T]
Returns an Observable that skips the first
numitems emitted by the source Observable and emits the remainder.Returns an Observable that skips the first
numitems emitted by the source Observable and emits the remainder.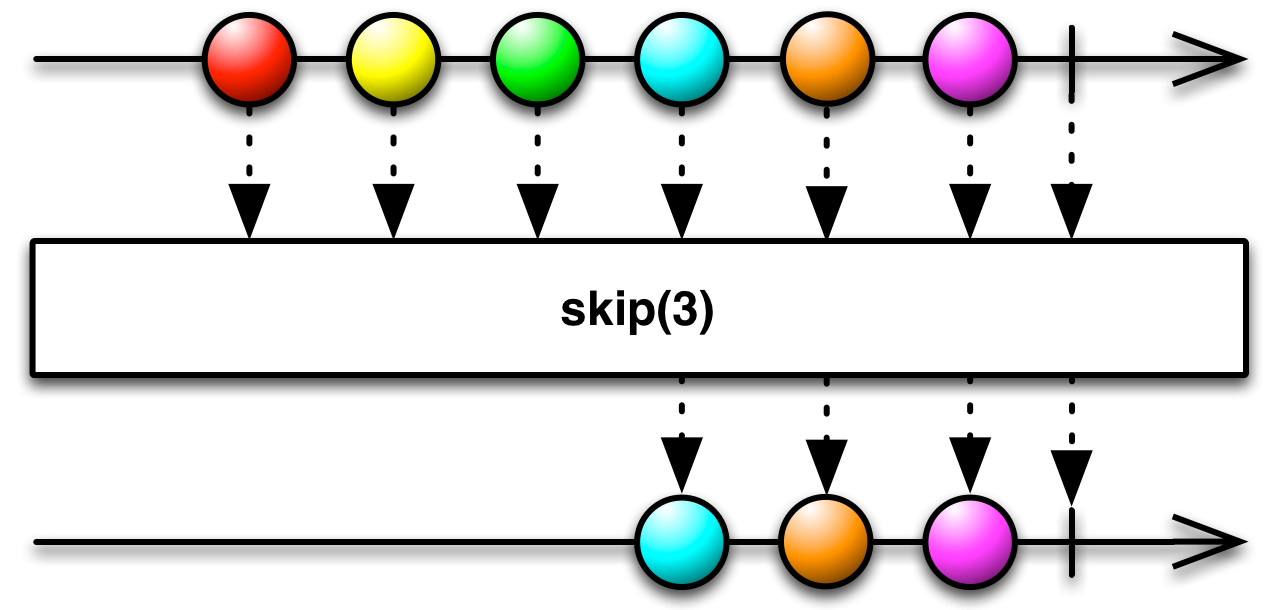
- total
the number of items to skip
- returns
an Observable that is identical to the source Observable except that it does not emit the first
numitems that the source emits
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
dropUntil[U](notifier: Observable[U]): Observable[T]
Returns an Observable that skips items emitted by the source Observable until a second Observable emits an item.
Returns an Observable that skips items emitted by the source Observable until a second Observable emits an item.
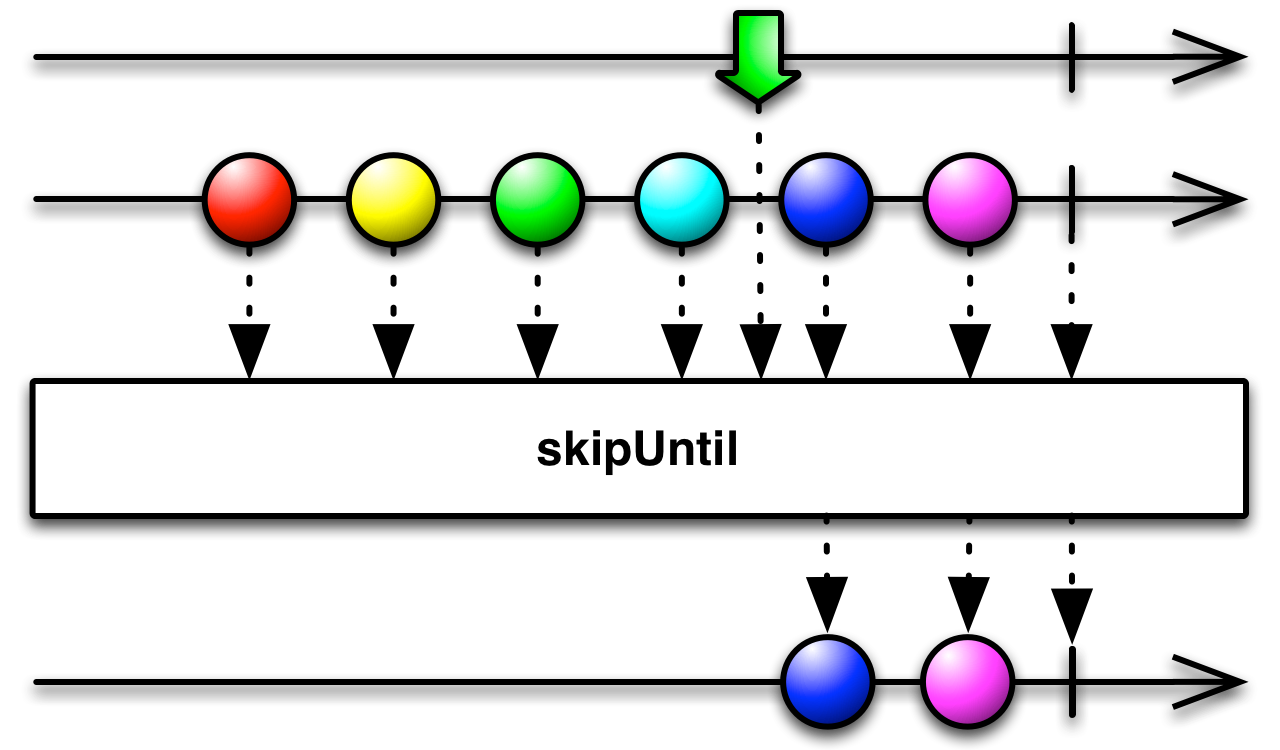
- notifier
the second Observable that has to emit an item before the source Observable's elements begin to be mirrored by the resulting Observable
- returns
an Observable that skips items from the source Observable until the second Observable emits an item, then emits the remaining items
- Definition Classes
- Observable
- See also
-
def
dropWhile(predicate: (T, Int) ⇒ Boolean): Observable[T]
Returns an Observable that bypasses all items from the source Observable as long as the specified condition holds true.
Returns an Observable that bypasses all items from the source Observable as long as the specified condition holds true. Emits all further source items as soon as the condition becomes false.
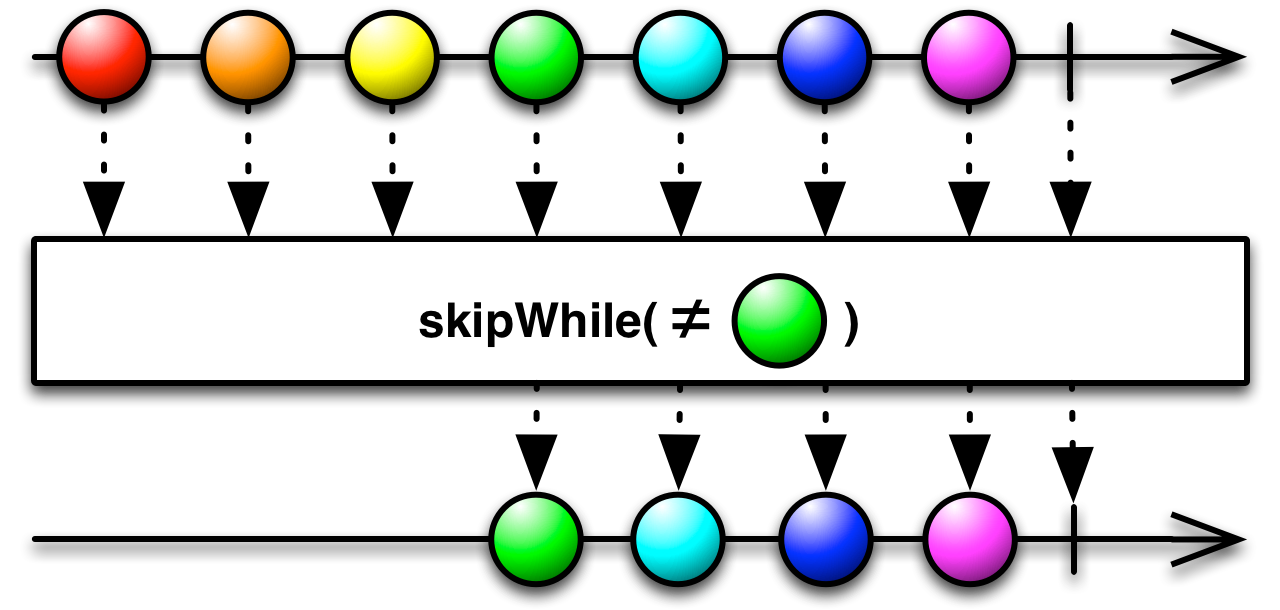
- predicate
A function to test each item emitted from the source Observable for a condition.
- returns
an Observable that emits all items from the source Observable as soon as the condition becomes false.
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
final
def
eq(arg0: AnyRef): Boolean
- Definition Classes
- AnyRef
-
def
equals(arg0: Any): Boolean
- Definition Classes
- AnyRef → Any
-
def
error(err: Any): Unit
Notifies the Observer that the rxscalajs.Observable has experienced an error condition.
Notifies the Observer that the rxscalajs.Observable has experienced an error condition.
If the rxscalajs.Observable calls this method, it will not thereafter call
nextorcompleted. -
def
every(predicate: (T, Int) ⇒ Boolean): Observable[Boolean]
Determines whether all elements of an observable sequence satisfy a condition.
Determines whether all elements of an observable sequence satisfy a condition.
- predicate
A function to test each element for a condition.
- returns
An observable sequence containing a single element determining whether all elements in the source sequence pass the test in the specified predicate.
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
exhaust[U](implicit evidence: <:<[Observable[T], Observable[Observable[U]]]): Observable[U]
Projects each source value to an Observable which is merged in the output Observable only if the previous projected Observable has completed.
Projects each source value to an Observable which is merged in the output Observable only if the previous projected Observable has completed. Maps each value to an Observable, then flattens all of these inner Observables using exhaust.

- returns
Returns an Observable that takes a source of Observables and propagates the first observable exclusively until it completes before subscribing to the next.
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
exhaustMap[R](project: (T, Int) ⇒ Observable[R]): Observable[R]
Converts a higher-order Observable into a first-order Observable by dropping inner Observables while the previous inner Observable has not yet completed.
Converts a higher-order Observable into a first-order Observable by dropping inner Observables while the previous inner Observable has not yet completed. Flattens an Observable-of-Observables by dropping the next inner Observables while the current inner is still executing.

- project
A function that, when applied to an item emitted by the source Observable, returns an Observable.
- returns
An Observable containing projected Observables of each item of the source, ignoring projected Observables that start before their preceding Observable has completed.
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
exhaustMap[I, R](project: (T, Int) ⇒ Observable[R], resultSelector: (T, I, Int, Int) ⇒ R): Observable[R]
Converts a higher-order Observable into a first-order Observable by dropping inner Observables while the previous inner Observable has not yet completed.
Converts a higher-order Observable into a first-order Observable by dropping inner Observables while the previous inner Observable has not yet completed. Flattens an Observable-of-Observables by dropping the next inner Observables while the current inner is still executing.

- project
A function that, when applied to an item emitted by the source Observable, returns an Observable.
- resultSelector
A function to produce the value on the output Observable based on the values and the indices of the source (outer) emission and the inner Observable emission. The arguments passed to this function are: outerValue: the value that came from the source innerValue: the value that came from the projected Observable outerIndex: the "index" of the value that came from the source innerIndex: the "index" of the value from the projected Observable
- returns
An Observable containing projected Observables of each item of the source, ignoring projected Observables that start before their preceding Observable has completed.
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
expand[R](project: (T, Int) ⇒ Observable[R]): Observable[R]
Returns an Observable where for each item in the source Observable, the supplied function is applied to each item, resulting in a new value to then be applied again with the function.
Returns an Observable where for each item in the source Observable, the supplied function is applied to each item, resulting in a new value to then be applied again with the function.
- project
the function for projecting the next emitted item of the Observable.
- returns
An observable sequence containing a single element determining whether all elements in the source sequence pass the test in the specified predicate.
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
expand[R](project: (T, Int) ⇒ Observable[R], scheduler: Scheduler, concurrent: Int = Int.MaxValue): Observable[R]
Returns an Observable where for each item in the source Observable, the supplied function is applied to each item, resulting in a new value to then be applied again with the function.
Returns an Observable where for each item in the source Observable, the supplied function is applied to each item, resulting in a new value to then be applied again with the function.
- project
the function for projecting the next emitted item of the Observable.
- scheduler
The Scheduler to use for managing the expansions.
- concurrent
the max number of observables that can be created concurrently. defaults to infinity.
- returns
An observable sequence containing a single element determining whether all elements in the source sequence pass the test in the specified predicate.
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
filter[T2](predicate: (T) ⇒ Boolean): Observable[T]
Returns an Observable which only emits those items for which a given predicate holds.
Returns an Observable which only emits those items for which a given predicate holds.
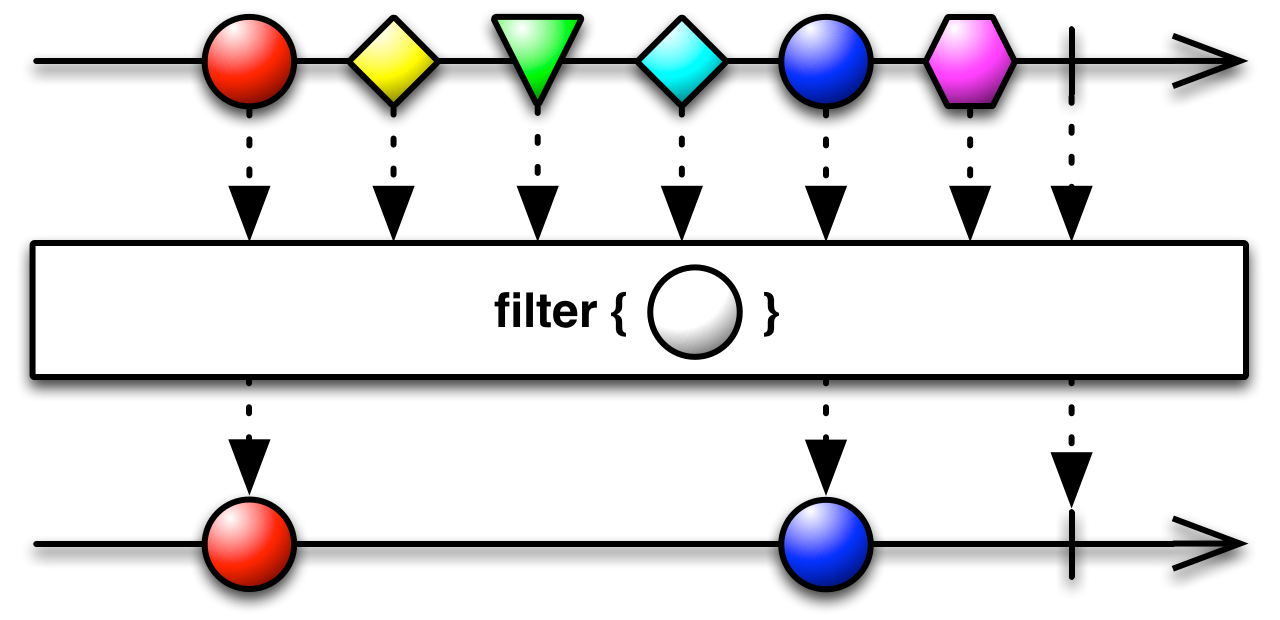
- predicate
a function that evaluates the items emitted by the source Observable, returning
trueif they pass the filter- returns
an Observable that emits only those items in the original Observable that the filter evaluates as
true
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
filter[T2](predicate: (T, Int) ⇒ Boolean): Observable[T]
Returns an Observable which only emits those items for which a given predicate holds.
Returns an Observable which only emits those items for which a given predicate holds.

- predicate
a function that evaluates the items emitted by the source Observable, returning
trueif they pass the filter- returns
an Observable that emits only those items in the original Observable that the filter evaluates as
true
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
finalize(): Unit
- Attributes
- protected[java.lang]
- Definition Classes
- AnyRef
- Annotations
- @throws( classOf[java.lang.Throwable] )
-
def
find[T2](predicate: (T, Int) ⇒ Boolean): Observable[T]
Emits only the first value emitted by the source Observable that meets some condition.
Emits only the first value emitted by the source Observable that meets some condition.

- predicate
A function called with each item to test for condition matching.
- returns
An Observable of the first item that matches the condition.
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
findIndex[T2](predicate: (T, Int) ⇒ Boolean): Observable[Int]
Emits only the index of the first value emitted by the source Observable that meets some condition.
Emits only the index of the first value emitted by the source Observable that meets some condition.

- predicate
A function called with each item to test for condition matching.
- returns
An Observable of the index of the first item that matches the condition.
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
first: Observable[T]
Returns an Observable that emits only the very first item emitted by the source Observable, or raises an
NoSuchElementExceptionif the source Observable is empty.Returns an Observable that emits only the very first item emitted by the source Observable, or raises an
NoSuchElementExceptionif the source Observable is empty.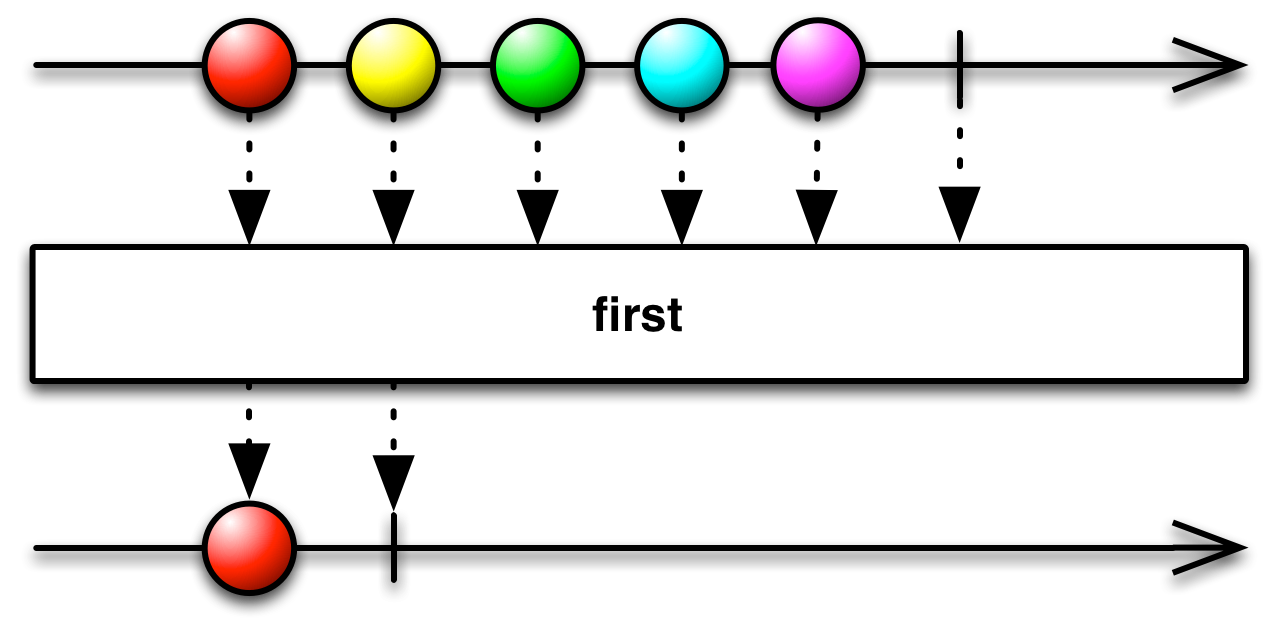
- returns
an Observable that emits only the very first item emitted by the source Observable, or raises an
NoSuchElementExceptionif the source Observable is empty
- Definition Classes
- Observable
- See also
"MSDN: Observable.firstAsync()"
-
def
firstOrElse[R >: T](default: ⇒ R): Observable[R]
Returns an Observable that emits only the very first item emitted by the source Observable, or a default value if the source Observable is empty.
Returns an Observable that emits only the very first item emitted by the source Observable, or a default value if the source Observable is empty.

- default
The default value to emit if the source Observable doesn't emit anything. This is a by-name parameter, so it is only evaluated if the source Observable doesn't emit anything.
- returns
an Observable that emits only the very first item from the source, or a default value if the source Observable completes without emitting any item.
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
flatMap[R](project: (T) ⇒ Observable[R]): Observable[R]
Returns an Observable that emits items based on applying a function that you supply to each item emitted by the source Observable , where that function returns an Observable , and then merging those resulting Observables and emitting the results of this merger, while limiting the maximum number of concurrent subscriptions to these Observables.
Returns an Observable that emits items based on applying a function that you supply to each item emitted by the source Observable , where that function returns an Observable , and then merging those resulting Observables and emitting the results of this merger, while limiting the maximum number of concurrent subscriptions to these Observables.

- project
a function that, when applied to an item emitted by the source Observable, returns an Observable
- returns
an Observable that emits the result of applying the transformation function to each item emitted by the source Observable and merging the results of the Observables obtained from this transformation
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
flatten[U](implicit evidence: <:<[Observable[T], Observable[Observable[U]]]): Observable[U]
Flattens the sequence of Observables emitted by
thisinto one Observable, without any transformation.Flattens the sequence of Observables emitted by
thisinto one Observable, without any transformation.
You can combine the items emitted by multiple Observables so that they act like a single Observable by using this method.
This operation is only available if
thisis of typeObservable[Observable[U]]for someU, otherwise you'll get a compilation error.- returns
an Observable that emits items that are the result of flattening the items emitted by the Observables emitted by
this
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
foldLeft[R](seed: R)(accumulator: (R, T) ⇒ R): Observable[R]
Returns an Observable that applies a function of your choosing to the first item emitted by a source Observable, then feeds the result of that function along with the second item emitted by an Observable into the same function, and so on until all items have been emitted by the source Observable, emitting the final result from the final call to your function as its sole item.
Returns an Observable that applies a function of your choosing to the first item emitted by a source Observable, then feeds the result of that function along with the second item emitted by an Observable into the same function, and so on until all items have been emitted by the source Observable, emitting the final result from the final call to your function as its sole item.
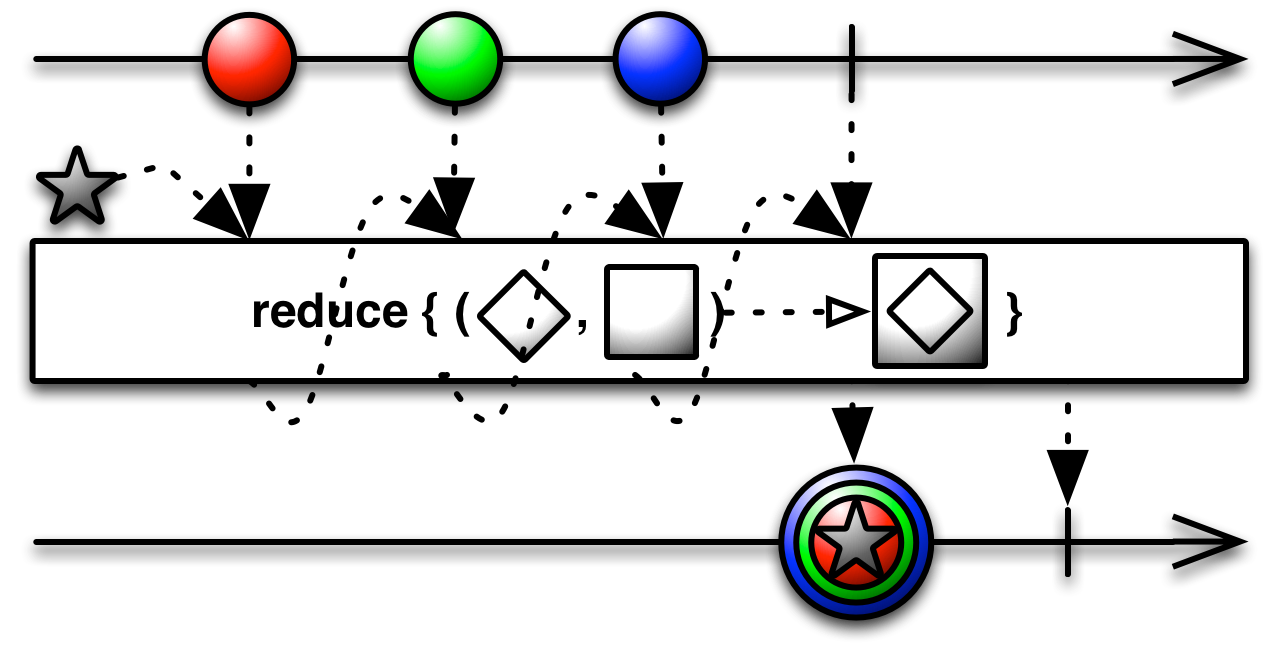
This technique, which is called "fold" or "reduce" here, is sometimes called "aggregate," "accumulate," "compress," or "inject" in other programming contexts. Groovy, for instance, has an
injectmethod that does a similar operation on lists.- seed
the initial (seed) accumulator value
- accumulator
an accumulator function to be invoked on each item emitted by the source Observable, the result of which will be used in the next accumulator call
- returns
an Observable that emits a single item that is the result of accumulating the output from the items emitted by the source Observable
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
final
def
getClass(): Class[_]
- Definition Classes
- AnyRef → Any
-
def
groupBy[K](keySelector: (T) ⇒ K): Observable[(K, Observable[T])]
Groups the items emitted by an Observable according to a specified criterion, and emits these grouped items as
(key, observable)pairs.Groups the items emitted by an Observable according to a specified criterion, and emits these grouped items as
(key, observable)pairs.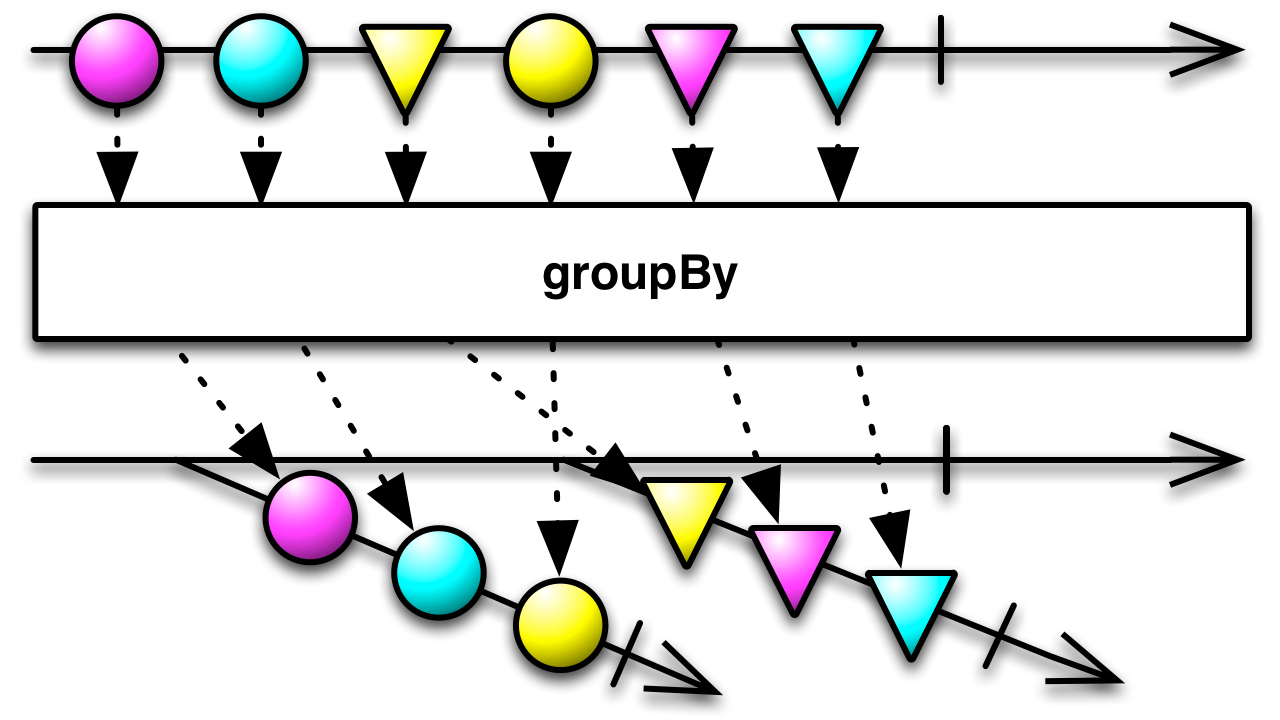
Note: A
(key, observable)will cache the items it is to emit until such time as it is subscribed to. For this reason, in order to avoid memory leaks, you should not simply ignore those(key, observable)pairs that do not concern you. Instead, you can signal to them that they may discard their buffers by applying an operator liketake(0)to them.- K
the key type
- keySelector
a function that extracts the key for each item
- returns
an Observable that emits
(key, observable)pairs, each of which corresponds to a unique key value and each of which emits those items from the source Observable that share that key value
- Definition Classes
- Observable
- See also
-
def
groupBy[K, V](keySelector: (T) ⇒ K, valueSelector: (T) ⇒ V): Observable[(K, Observable[V])]
Groups the items emitted by an Observable according to a specified criterion, and emits these grouped items as
(key, observable)pairs.Groups the items emitted by an Observable according to a specified criterion, and emits these grouped items as
(key, observable)pairs.
Note: A
(key, observable)will cache the items it is to emit until such time as it is subscribed to. For this reason, in order to avoid memory leaks, you should not simply ignore those(key, observable)pairs that do not concern you. Instead, you can signal to them that they may discard their buffers by applying an operator liketake(0)to them.- K
the key type
- V
the value type
- keySelector
a function that extracts the key for each item
- valueSelector
a function that extracts the return element for each item
- returns
an Observable that emits
(key, observable)pairs, each of which corresponds to a unique key value and each of which emits those items from the source Observable that share that key value
- Definition Classes
- Observable
- See also
-
def
hashCode(): Int
- Definition Classes
- AnyRef → Any
-
def
ignoreElements: Observable[T]
Ignores all items emitted by the source Observable and only passes calls of complete or error.
Ignores all items emitted by the source Observable and only passes calls of complete or error.

- returns
an empty Observable that only calls complete or error, based on which one is called by the source Observable.
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
val
inner: ObservableFacade[T]
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
isEmpty: Observable[Boolean]
Tests whether this
Observableemits no elements.Tests whether this
Observableemits no elements.- returns
an Observable emitting one single Boolean, which is
trueif thisObservableemits no elements, andfalseotherwise.
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
final
def
isInstanceOf[T0]: Boolean
- Definition Classes
- Any
-
def
last: Observable[T]
Returns an Observable that emits the last item emitted by the source Observable or notifies observers of an
NoSuchElementExceptionif the source Observable is empty.Returns an Observable that emits the last item emitted by the source Observable or notifies observers of an
NoSuchElementExceptionif the source Observable is empty.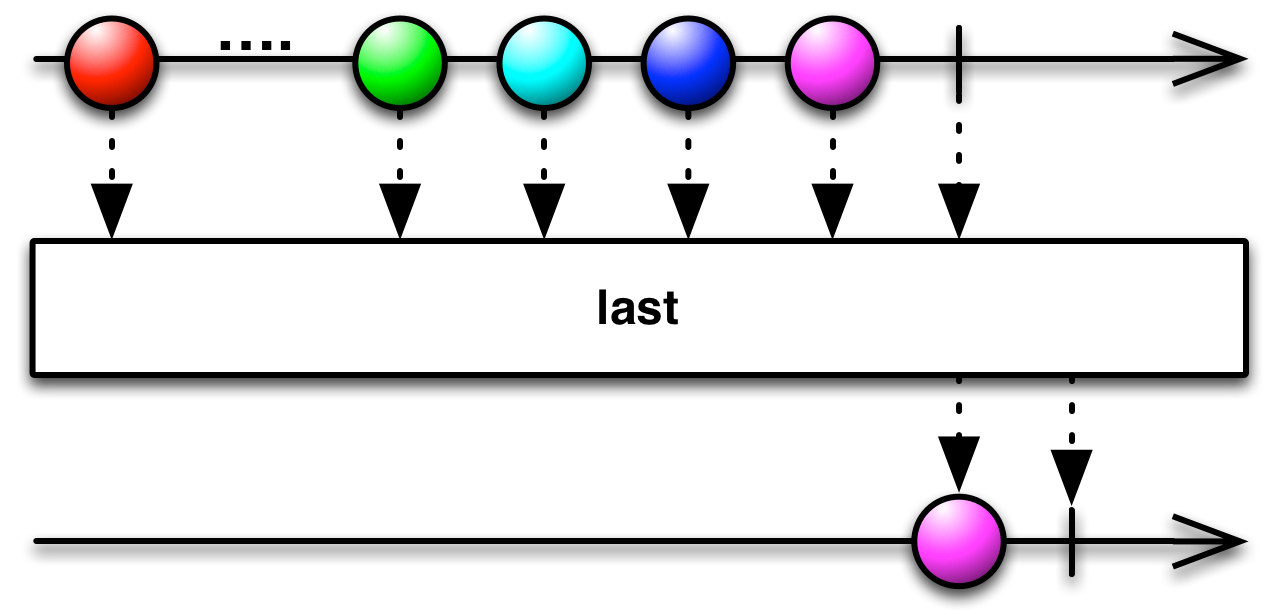
- returns
an Observable that emits the last item from the source Observable or notifies observers of an error
- Definition Classes
- Observable
- See also
"MSDN: Observable.lastAsync()"
-
def
lastOrElse[R >: T](default: ⇒ R): Observable[R]
Returns an Observable that emits only the last item emitted by the source Observable, or a default item if the source Observable completes without emitting any items.
Returns an Observable that emits only the last item emitted by the source Observable, or a default item if the source Observable completes without emitting any items.

- default
the default item to emit if the source Observable is empty. This is a by-name parameter, so it is only evaluated if the source Observable doesn't emit anything.
- returns
an Observable that emits only the last item emitted by the source Observable, or a default item if the source Observable is empty
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
map[R](project: (T) ⇒ R): Observable[R]
Returns an Observable that applies the given function to each item emitted by an Observable and emits the result.
Returns an Observable that applies the given function to each item emitted by an Observable and emits the result.
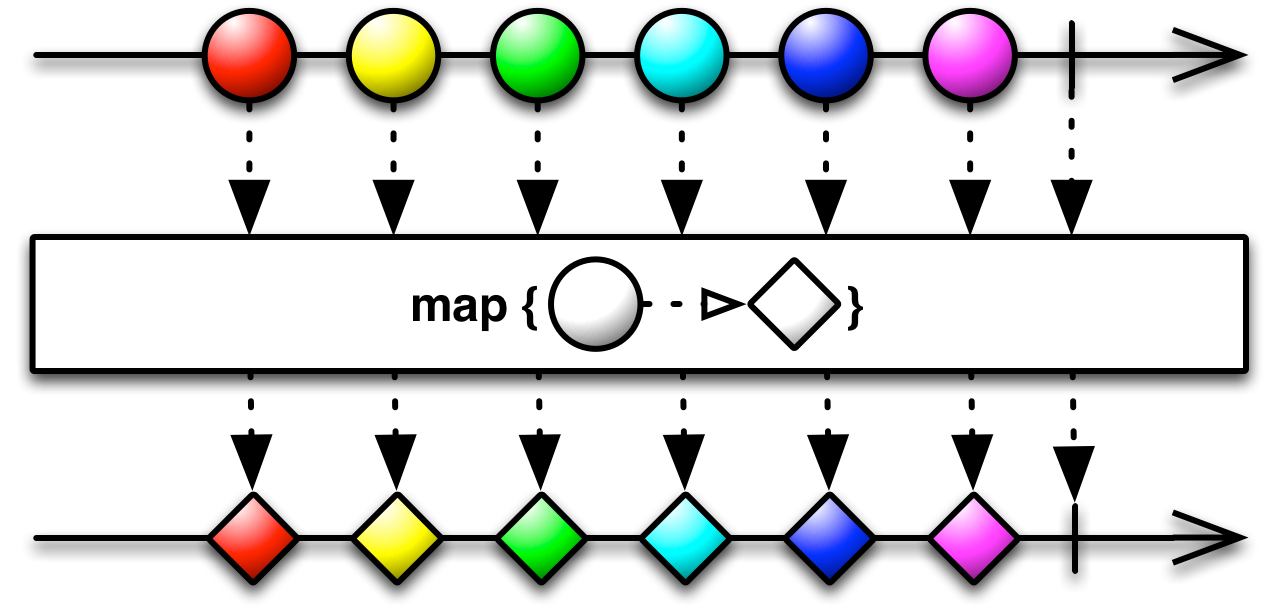
- project
a function to apply to each item emitted by the Observable
- returns
an Observable that emits the items from the source Observable, transformed by the given function
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
mapTo[R](value: R): Observable[R]
Returns an Observable that maps each element to a specific value.
Returns an Observable that maps each element to a specific value.

- value
the value to map to.
- returns
an Observable that emits the items from the source Observable, transformed by the given function
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
mapWithIndex[R](project: (T, Int) ⇒ R): Observable[R]
Returns an Observable that applies the given function to each item emitted by an Observable and emits the result.
Returns an Observable that applies the given function to each item emitted by an Observable and emits the result.

- project
a function to apply to each item emitted by the Observable
- returns
an Observable that emits the items from the source Observable, transformed by the given function
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
materialize: Observable[Notification[_ <: T]]
Turns all of the notifications from a source Observable into onNext emissions, and marks them with their original notification types within rxscalajs.Notification objects.
Turns all of the notifications from a source Observable into onNext emissions, and marks them with their original notification types within rxscalajs.Notification objects.
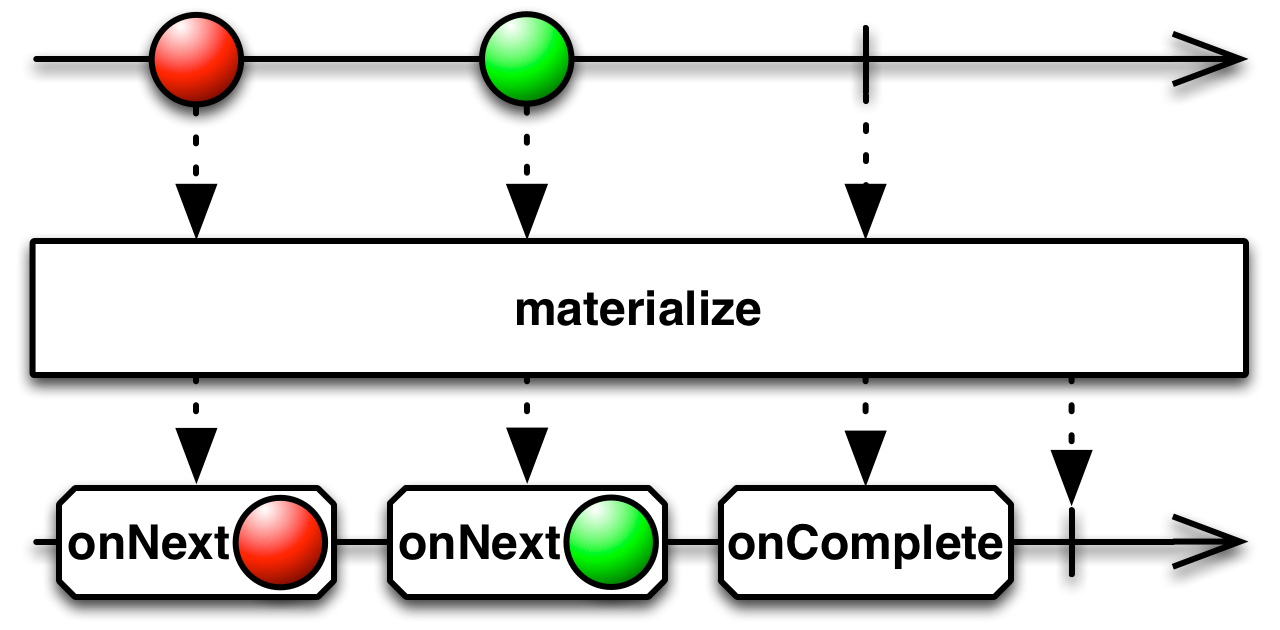
- returns
an Observable whose items are the result of materializing the items and notifications of the source Observable
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
merge[R >: T](first: Observable[R], second: Observable[R], third: Observable[R]): Observable[R]
Flattens four Observables into one Observable, without any transformation.
Flattens four Observables into one Observable, without any transformation.
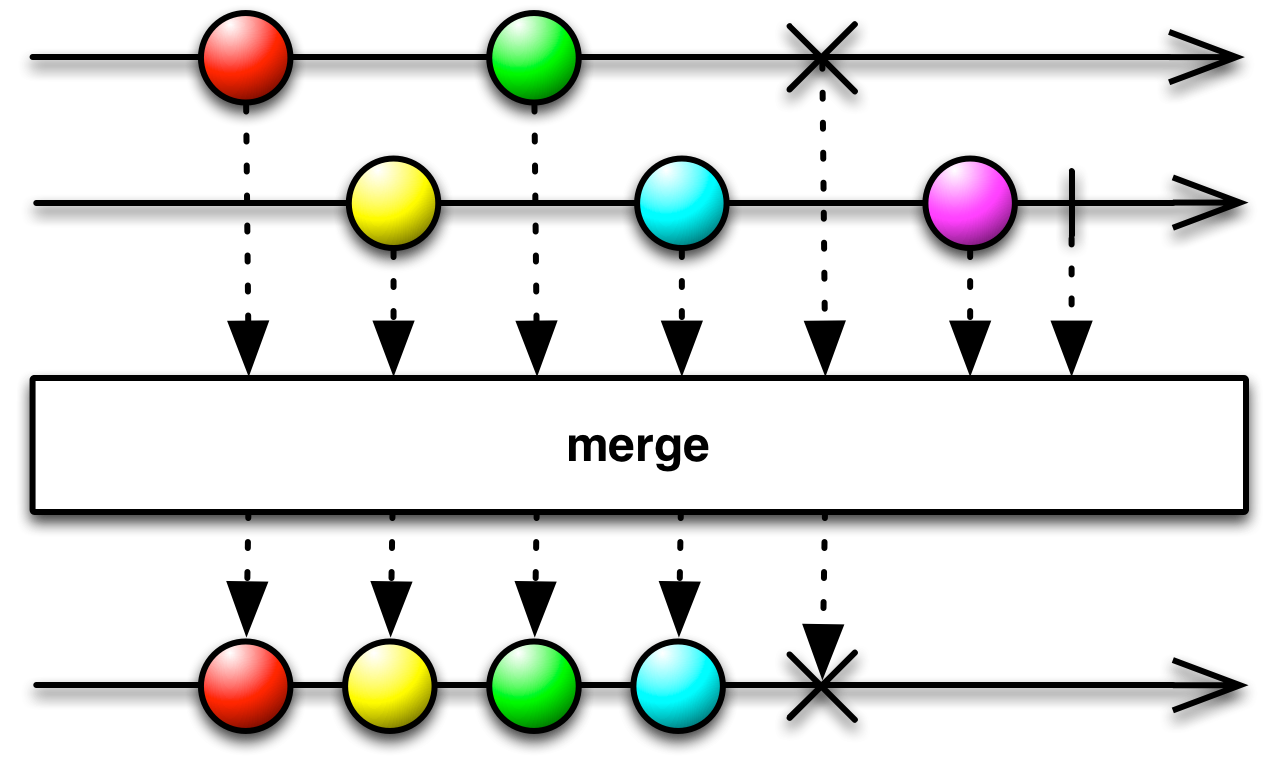
You can combine items emitted by four Observables so that they act like a single Observable by using the
mergemethod.- first
an Observable to be merged
- second
an Observable to be merged
- third
an Observable to be merged
- returns
an Observable that emits items from all Observables until one emits
onErroror all Observables emitonCompleted.
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
merge[R >: T](first: Observable[R], second: Observable[R]): Observable[R]
Flattens three Observables into one Observable, without any transformation.
Flattens three Observables into one Observable, without any transformation.

You can combine items emitted by three Observables so that they act like a single Observable by using the
mergemethod.- first
an Observable to be merged
- second
an Observable to be merged
- returns
an Observable that emits items from all Observables until one emits
onErroror all Observables emitonCompleted.
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
merge[R >: T](that: Observable[R]): Observable[R]
Flattens two Observables into one Observable, without any transformation.
Flattens two Observables into one Observable, without any transformation.

You can combine items emitted by two Observables so that they act like a single Observable by using the
mergemethod.- that
an Observable to be merged
- returns
an Observable that emits items from
thisandthatuntilthisorthatemitsonErroror both Observables emitonCompleted.
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
merge[R >: T](that: Observable[R], concurrent: Int = Int.MaxValue, scheduler: Scheduler): Observable[R]
Flattens two Observables into one Observable, without any transformation.
Flattens two Observables into one Observable, without any transformation.

You can combine items emitted by two Observables so that they act like a single Observable by using the
mergemethod.- that
an Observable to be merged
- concurrent
the maximum number of Observables that may be subscribed to concurrently
- returns
an Observable that emits items from
thisandthatuntilthisorthatemitsonErroror both Observables emitonCompleted.
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
mergeAll[U](concurrent: Int = Int.MaxValue)(implicit evidence: <:<[Observable[T], Observable[Observable[U]]]): Observable[U]
Flattens the sequence of Observables emitted by
thisinto one Observable, without any transformation.Flattens the sequence of Observables emitted by
thisinto one Observable, without any transformation.
You can combine the items emitted by multiple Observables so that they act like a single Observable by using this method.
This operation is only available if
thisis of typeObservable[Observable[U]]for someU, otherwise you'll get a compilation error.- concurrent
the maximum number of Observables that may be subscribed to concurrently
- returns
an Observable that emits items that are the result of flattening the items emitted by the Observables emitted by
this
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
mergeMap[R](project: (T) ⇒ Observable[R]): Observable[R]
Returns an Observable that emits items based on applying a function that you supply to each item emitted by the source Observable , where that function returns an Observable , and then merging those resulting Observables and emitting the results of this merger, while limiting the maximum number of concurrent subscriptions to these Observables.
Returns an Observable that emits items based on applying a function that you supply to each item emitted by the source Observable , where that function returns an Observable , and then merging those resulting Observables and emitting the results of this merger, while limiting the maximum number of concurrent subscriptions to these Observables.

- project
a function that, when applied to an item emitted by the source Observable, returns an Observable
- returns
an Observable that emits the result of applying the transformation function to each item emitted by the source Observable and merging the results of the Observables obtained from this transformation
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
mergeMapTo[R](innerObservable: Observable[R]): Observable[R]
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
mergeMapTo[I, R](innerObservable: Observable[I], resultSelector: (T, I, Int, Int) ⇒ R, concurrent: Int = Int.MaxValue): Observable[R]
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
multicast(subjectOrSubjectFactory: SubjectFacade[_ >: T]): ConnectableObservable[T]
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
final
def
ne(arg0: AnyRef): Boolean
- Definition Classes
- AnyRef
-
def
next(value: T): Unit
Provides the Observer with new data.
Provides the Observer with new data.
The rxscalajs.Observable calls this closure 0 or more times.
The rxscalajs.Observable will not call this method again after it calls either
completedorerror. -
final
def
notify(): Unit
- Definition Classes
- AnyRef
-
final
def
notifyAll(): Unit
- Definition Classes
- AnyRef
-
def
onErrorResumeNext[U >: T](resumeFunction: (Any) ⇒ Observable[U]): Observable[U]
Instruct an Observable to pass control to another Observable rather than invoking
onErrorif it encounters an error.Instruct an Observable to pass control to another Observable rather than invoking
onErrorif it encounters an error.
By default, when an Observable encounters an error that prevents it from emitting the expected item to its Observer, the Observable invokes its Observer's
onErrormethod, and then quits without invoking any more of its Observer's methods. TheonErrorResumeNextmethod changes this behavior. If you pass a function that returns an Observable (resumeFunction) toonErrorResumeNext, if the original Observable encounters an error, instead of invoking its Observer'sonErrormethod, it will instead relinquish control to the Observable returned fromresumeFunction, which will invoke the Observer'sonNextmethod if it is able to do so. In such a case, because no Observable necessarily invokesonError, the Observer may never know that an error happened.You can use this to prevent errors from propagating or to supply fallback data should errors be encountered.
- resumeFunction
a function that returns an Observable that will take over if the source Observable encounters an error
- returns
the original Observable, with appropriately modified behavior
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
onErrorReturn[U >: T](resumeFunction: (Any) ⇒ U): Observable[U]
Instruct an Observable to emit an item (returned by a specified function) rather than invoking
onErrorif it encounters an error.Instruct an Observable to emit an item (returned by a specified function) rather than invoking
onErrorif it encounters an error.
By default, when an Observable encounters an error that prevents it from emitting the expected item to its
Observer, the Observable invokes its Observer'sonErrormethod, and then quits without invoking any more of its Observer's methods. TheonErrorReturnmethod changes this behavior. If you pass a function (resumeFunction) to an Observable'sonErrorReturnmethod, if the original Observable encounters an error, instead of invoking its Observer'sonErrormethod, it will instead pass the return value ofresumeFunctionto the Observer'sonNextmethod.You can use this to prevent errors from propagating or to supply fallback data should errors be encountered.
- resumeFunction
a function that returns an item that the new Observable will emit if the source Observable encounters an error
- returns
the original Observable with appropriately modified behavior
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
orElse[U >: T](default: ⇒ U): Observable[U]
Returns an Observable that emits the items emitted by the source Observable or a specified default item if the source Observable is empty.
Returns an Observable that emits the items emitted by the source Observable or a specified default item if the source Observable is empty.

- default
the item to emit if the source Observable emits no items. This is a by-name parameter, so it is only evaluated if the source Observable doesn't emit anything.
- returns
an Observable that emits either the specified default item if the source Observable emits no items, or the items emitted by the source Observable
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
pairwise: Observable[(T, T)]
Groups pairs of consecutive emissions together and emits them as a tuple of two values.
Groups pairs of consecutive emissions together and emits them as a tuple of two values.

- returns
an Observable of pairs (as tuples) of consecutive values from the source Observable.
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
partition[T2](predicate: (T) ⇒ Boolean): (Observable[T], Observable[T])
Splits the source Observable into two, one with values that satisfy a predicate, and another with values that don't satisfy the predicate.
Splits the source Observable into two, one with values that satisfy a predicate, and another with values that don't satisfy the predicate. It's like filter, but returns two Observables: one like the output of filter, and the other with values that did not pass the condition.

- predicate
A function that evaluates each value emitted by the source Observable. If it returns true, the value is emitted on the first Observable in the returned array, if false the value is emitted on the second Observable in the tuple.
- returns
an Observable that emits a single item that is the result of accumulating the output from the items emitted by the source Observable
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
publish: ConnectableObservable[T]
Returns a ConnectableObservable, which waits until the
connectfunction is called before it begins emitting items fromthis[Observable to those Observers that have subscribed to it.Returns a ConnectableObservable, which waits until the
connectfunction is called before it begins emitting items fromthis[Observable to those Observers that have subscribed to it.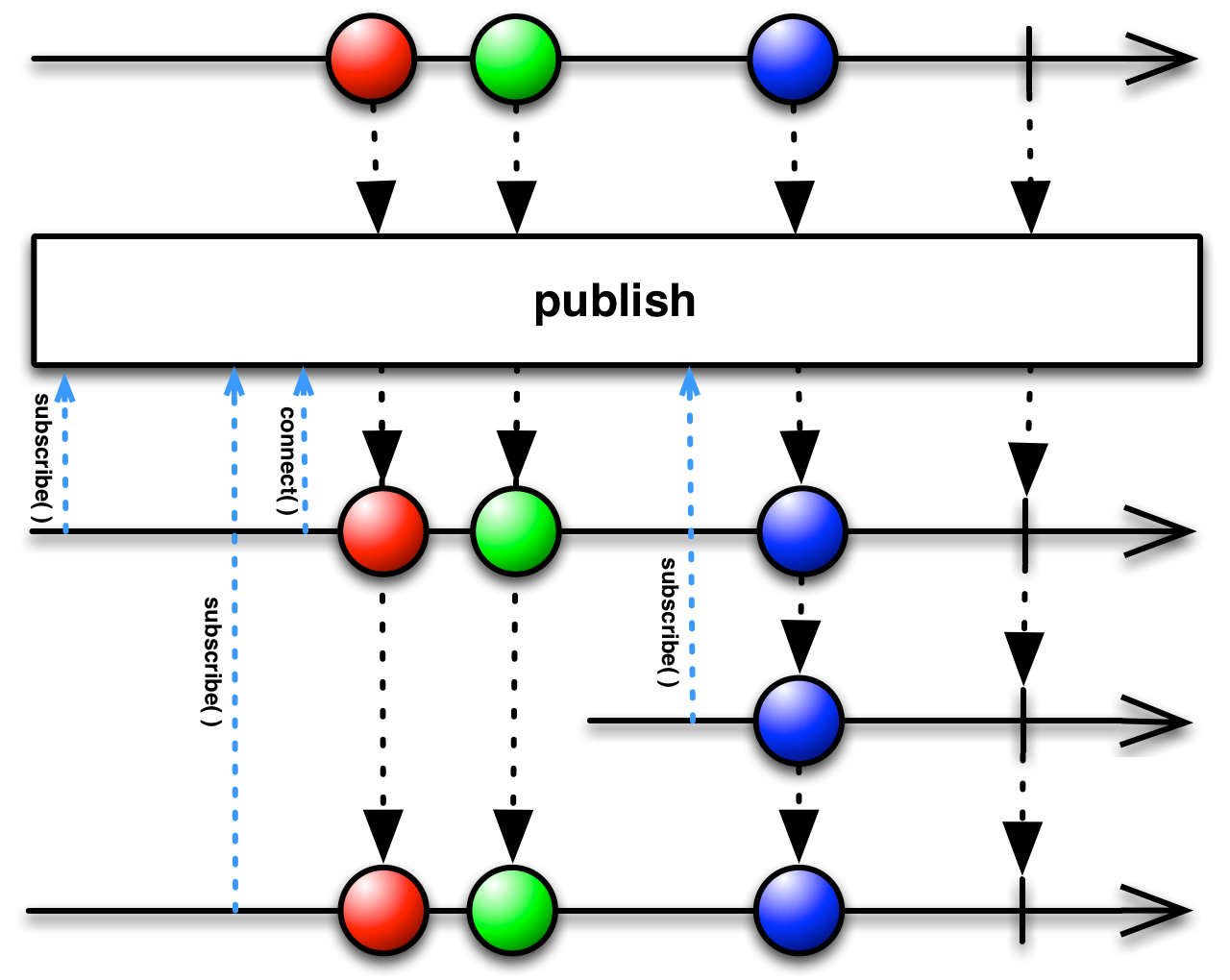
- returns
an ConnectableObservable
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
publishLast: ConnectableObservable[T]
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
publishReplay(bufferSize: Int = Int.MaxValue, windowTime: FiniteDuration = Int.MaxValue.millis): ConnectableObservable[T]
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
race(observables: Observable[_ >: T]*): Observable[T]
Returns an Observable that mirrors the first source Observable to emit an item from the combination of this Observable and supplied Observables
Returns an Observable that mirrors the first source Observable to emit an item from the combination of this Observable and supplied Observables
- observables
sources used to race for which Observable emits first.
- returns
an Observable that mirrors the output of the first Observable to emit an item.
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
reduce[U >: T](accumulator: (U, U) ⇒ U): Observable[U]
Returns an Observable that applies a function of your choosing to the first item emitted by a source Observable, then feeds the result of that function along with the second item emitted by the source Observable into the same function, and so on until all items have been emitted by the source Observable, and emits the final result from the final call to your function as its sole item.
Returns an Observable that applies a function of your choosing to the first item emitted by a source Observable, then feeds the result of that function along with the second item emitted by the source Observable into the same function, and so on until all items have been emitted by the source Observable, and emits the final result from the final call to your function as its sole item.
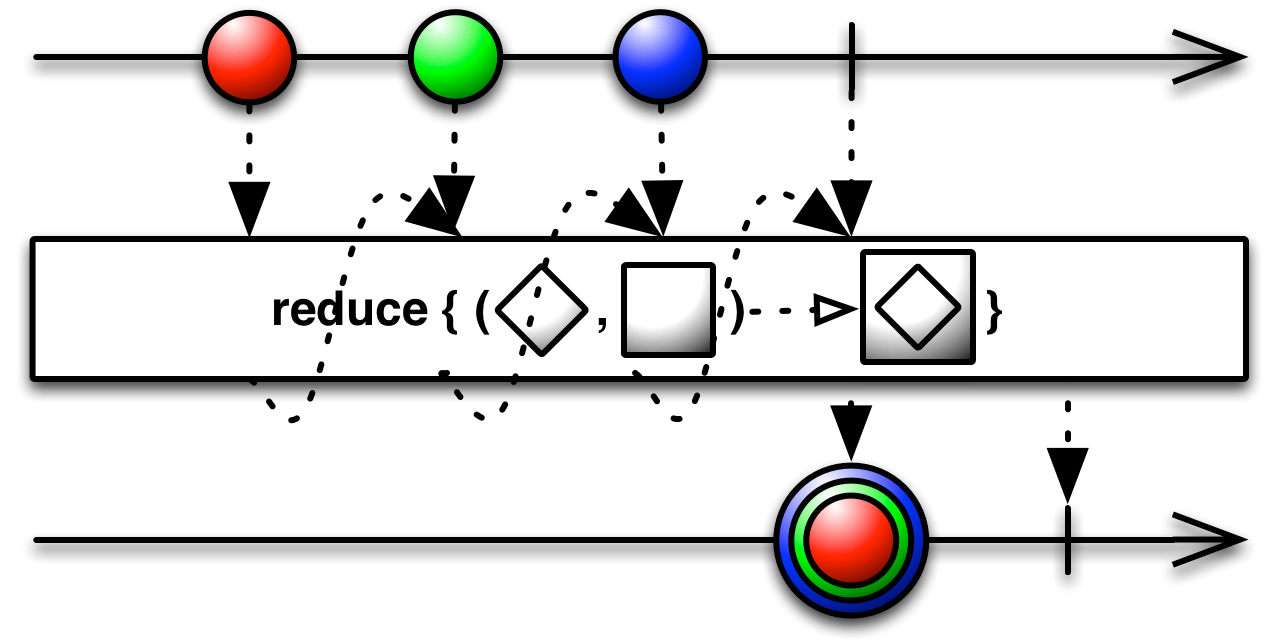
This technique, which is called "reduce" or "aggregate" here, is sometimes called "fold," "accumulate," "compress," or "inject" in other programming contexts. Groovy, for instance, has an
injectmethod that does a similar operation on lists.- accumulator
An accumulator function to be invoked on each item emitted by the source Observable, whose result will be used in the next accumulator call
- returns
an Observable that emits a single item that is the result of accumulating the output from the source Observable
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
repeat(count: Int = 1): Observable[T]
Returns an Observable that repeats the sequence of items emitted by the source Observable at most
counttimes.Returns an Observable that repeats the sequence of items emitted by the source Observable at most
counttimes.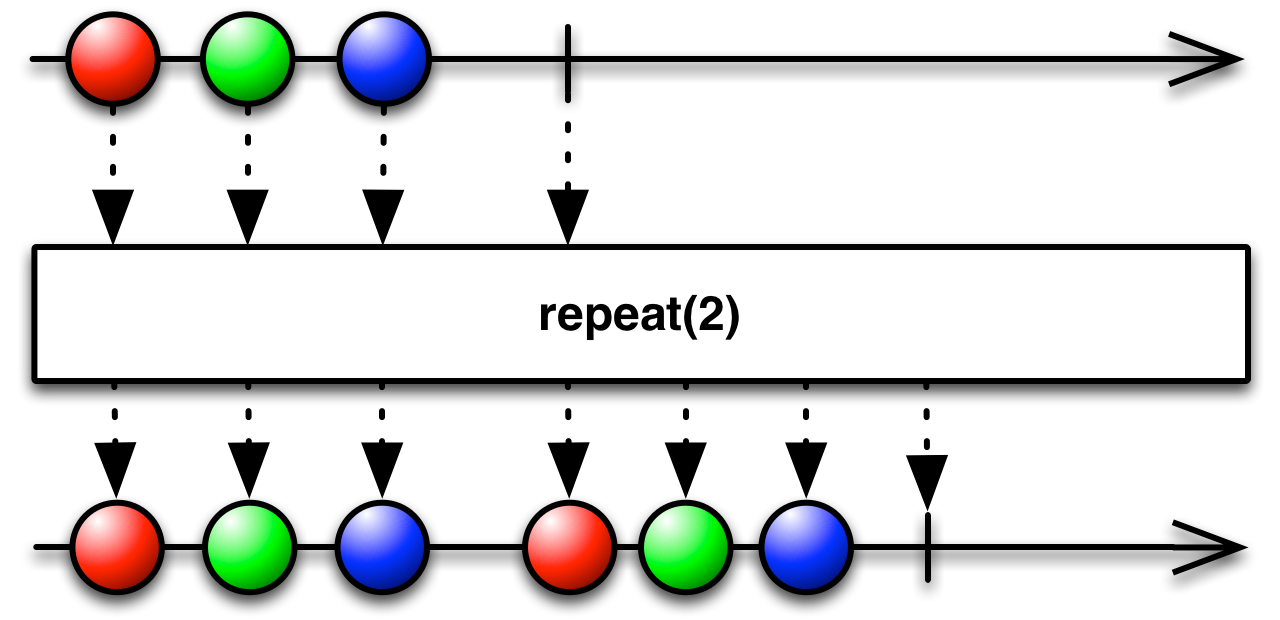
- count
the number of times the source Observable items are repeated, a count of 0 will yield an empty sequence
- returns
an Observable that repeats the sequence of items emitted by the source Observable at most
counttimes
- Definition Classes
- Observable
- See also
-
def
retry(count: Int = 1): Observable[T]
Retry subscription to origin Observable upto given retry count.
Retry subscription to origin Observable upto given retry count.
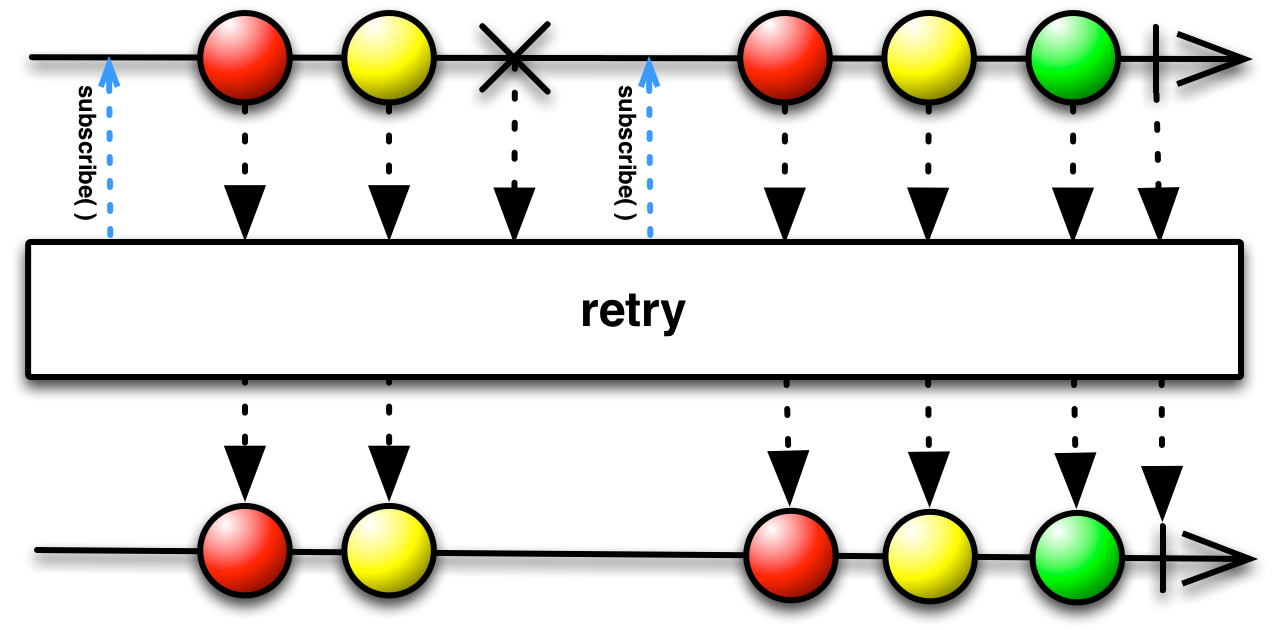
If Observer.onError is invoked the source Observable will be re-subscribed to as many times as defined by retryCount.
Any Observer.onNext calls received on each attempt will be emitted and concatenated together.
For example, if an Observable fails on first time but emits [1, 2] then succeeds the second time and emits [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] then the complete output would be [1, 2, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, onCompleted].
- count
Number of retry attempts before failing.
- returns
Observable with retry logic.
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
retryWhen[U, S](notifier: (Observable[U]) ⇒ Observable[S]): Observable[T]
Returns an Observable that emits the same values as the source observable with the exception of an
onError.Returns an Observable that emits the same values as the source observable with the exception of an
onError. AnonErrornotification from the source will result in the emission of aThrowableto the Observable provided as an argument to thenotificationHandlerfunction. If the Observable returnedonCompletesoronErrorsthenretrywill callonCompletedoronErroron the child subscription. Otherwise, this Observable will resubscribe to the source Observable.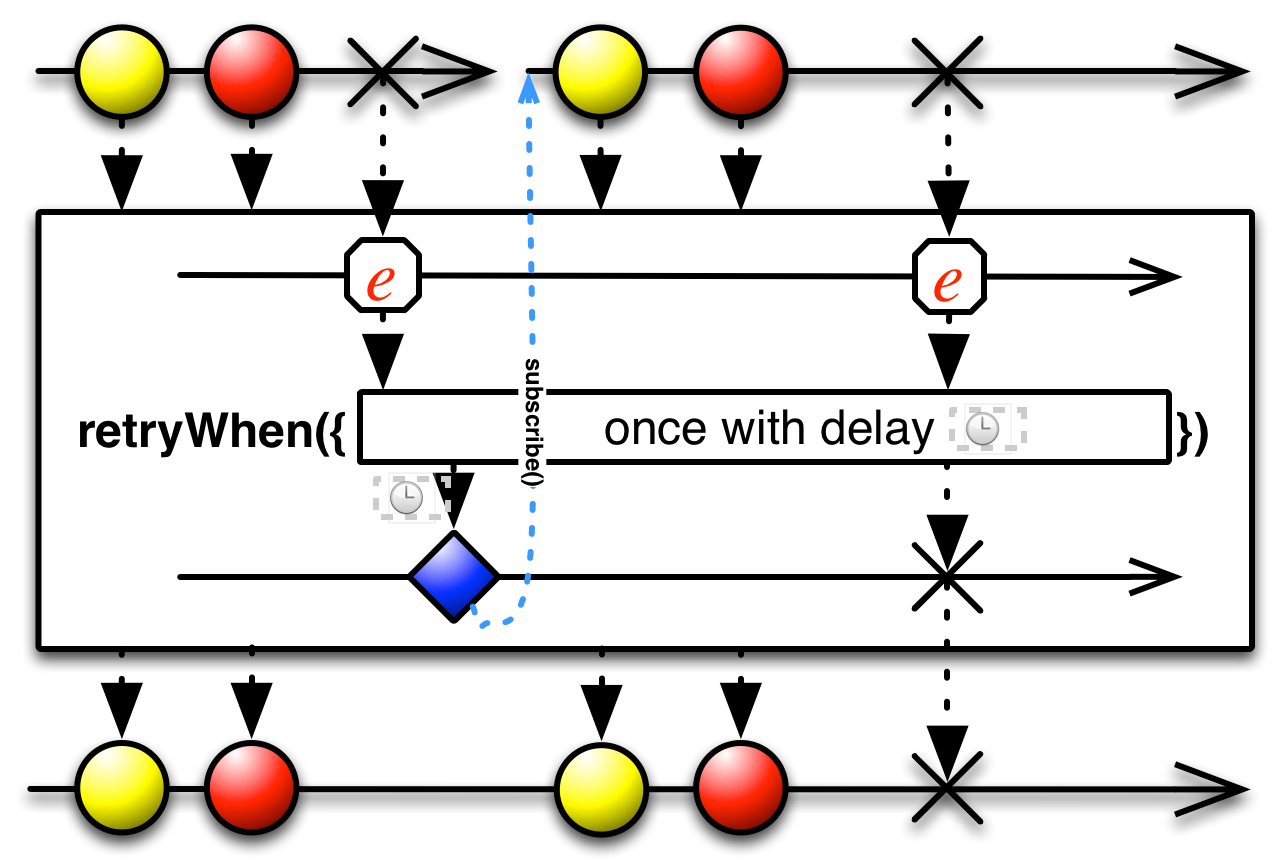
Example:
This retries 3 times, each time incrementing the number of seconds it waits.
- notifier
receives an Observable of a Throwable with which a user can complete or error, aborting the retry
- returns
the source Observable modified with retry logic
- Definition Classes
- Observable
This retries 3 times, each time incrementing the number of seconds it waits.
Observable[String]({ subscriber => println("subscribing") subscriber.onError(new RuntimeException("always fails")) }).retryWhen({ throwableObservable => throwableObservable.zipWith(Observable.from(1 to 3))((t, i) => i).flatMap(i => { println("delay retry by " + i + " second(s)") Observable.timer(Duration(i, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) }) }).toBlocking.foreach(s => println(s))
Output is:
subscribing delay retry by 1 second(s) subscribing delay retry by 2 second(s) subscribing delay retry by 3 second(s) subscribing
<dl> <dt>Scheduler:</dt>
- `retryWhen` operates by default on the `trampoline` [[Scheduler]].
</dl>- Since
0.20
- See also
RxScalaDemo.retryWhenDifferentExceptionsExample for a more intricate example
Example: -
def
sample[I](sampler: Observable[I]): Observable[T]
Return an Observable that emits the results of sampling the items emitted by the source Observable whenever the specified sampler Observable emits an item or completes.
Return an Observable that emits the results of sampling the items emitted by the source Observable whenever the specified sampler Observable emits an item or completes.
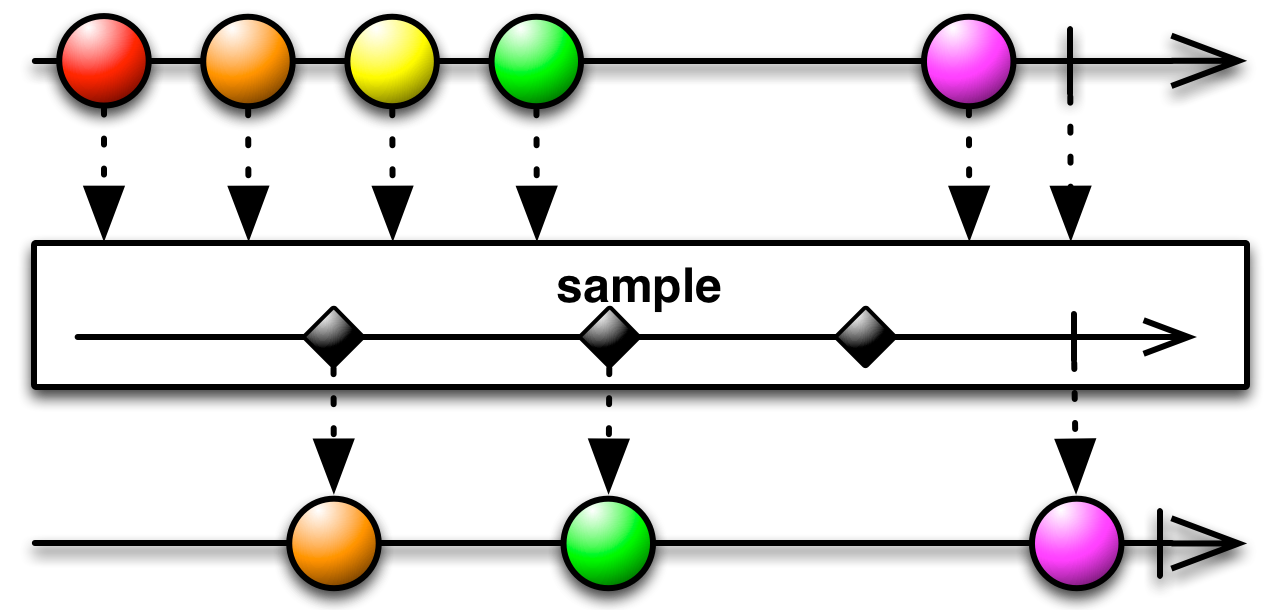
- sampler
the Observable to use for sampling the source Observable
- returns
an Observable that emits the results of sampling the items emitted by this Observable whenever the sampler Observable emits an item or completes
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
sampleTime(delay: Int): Observable[T]
Returns an Observable that emits the results of sampling the items emitted by the source Observable at a specified time interval.
Returns an Observable that emits the results of sampling the items emitted by the source Observable at a specified time interval.

- delay
the sampling rate
- returns
an Observable that emits the results of sampling the items emitted by the source Observable at the specified time interval
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
sampleTime(delay: FiniteDuration): Observable[T]
Returns an Observable that emits the results of sampling the items emitted by the source Observable at a specified time interval.
Returns an Observable that emits the results of sampling the items emitted by the source Observable at a specified time interval.

- delay
the sampling rate
- returns
an Observable that emits the results of sampling the items emitted by the source Observable at the specified time interval
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
sampleTime(delay: FiniteDuration, scheduler: Scheduler): Observable[T]
Returns an Observable that emits the results of sampling the items emitted by the source Observable at a specified time interval.
Returns an Observable that emits the results of sampling the items emitted by the source Observable at a specified time interval.

- delay
the sampling rate
- scheduler
the rxscalajs.Scheduler to use when sampling
- returns
an Observable that emits the results of sampling the items emitted by the source Observable at the specified time interval
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
scan[U >: T](accumulator: (U, U) ⇒ U): Observable[U]
Returns an Observable that applies a function of your choosing to the first item emitted by a source Observable, then feeds the result of that function along with the second item emitted by an Observable into the same function, and so on until all items have been emitted by the source Observable, emitting the result of each of these iterations.
Returns an Observable that applies a function of your choosing to the first item emitted by a source Observable, then feeds the result of that function along with the second item emitted by an Observable into the same function, and so on until all items have been emitted by the source Observable, emitting the result of each of these iterations.
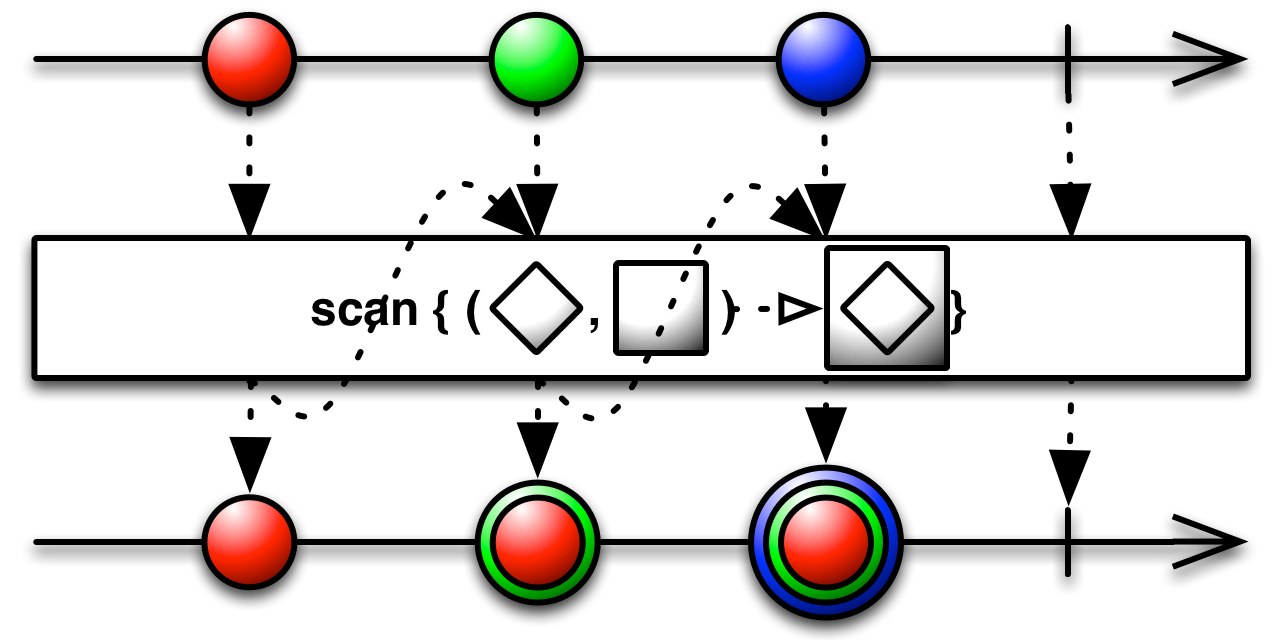
This sort of function is sometimes called an accumulator.
Note that when you pass a seed to
scan()the resulting Observable will emit that seed as its first emitted item.- accumulator
an accumulator function to be invoked on each item emitted by the source Observable, whose result will be emitted to rxscalajs.subscription.ObserverFacades via onNext and used in the next accumulator call.
- returns
an Observable that emits the results of each call to the accumulator function
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
scan[R](seed: R)(accumulator: (R, T) ⇒ R): Observable[R]
Returns an Observable that applies a function of your choosing to the first item emitted by a source Observable, then feeds the result of that function along with the second item emitted by an Observable into the same function, and so on until all items have been emitted by the source Observable, emitting the result of each of these iterations.
Returns an Observable that applies a function of your choosing to the first item emitted by a source Observable, then feeds the result of that function along with the second item emitted by an Observable into the same function, and so on until all items have been emitted by the source Observable, emitting the result of each of these iterations.
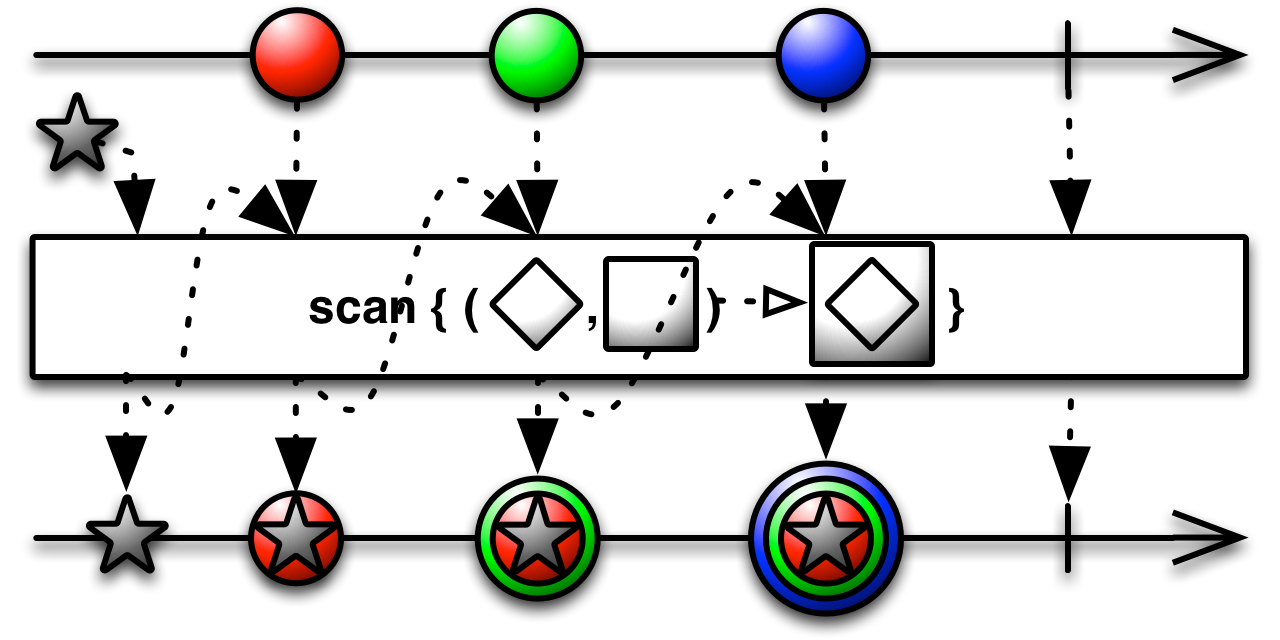
This sort of function is sometimes called an accumulator.
Note that when you pass a seed to
scan()the resulting Observable will emit that seed as its first emitted item.- seed
the initial (seed) accumulator value
- accumulator
an accumulator function to be invoked on each item emitted by the source Observable, whose result will be emitted to rxscalajs.subscription.ObserverFacades via onNext and used in the next accumulator call.
- returns
an Observable that emits the results of each call to the accumulator function
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
scanM[M[_], R](seed: R)(accumulator: (R, T) ⇒ M[R])(implicit arg0: Monad[M]): Observable[M[R]]
Similar to scan, but uses monadic accumulation instead.
Similar to scan, but uses monadic accumulation instead.
- seed
the initial (seed) accumulator value
- accumulator
an accumulator function to be invoked on each item emitted by the source
- returns
an Observable that emits the monadic result of each call to the accumulator function
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
scanMap[R](f: (T) ⇒ R)(implicit arg0: Monoid[R]): Observable[R]
Similar to scan, but uses a monoid for accumulation instead.
Similar to scan, but uses a monoid for accumulation instead.
- f
a function to map this Observable to a monoid
- returns
an Observable that emits the result of the accumulation
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
share: Observable[T]
Returns a new Observable that multicasts (shares) the original Observable.
Returns a new Observable that multicasts (shares) the original Observable. As long a there is more than 1 rxscalajs.subscription.Subscriber, this Observable will be subscribed and emitting data. When all subscribers have unsubscribed it will unsubscribe from the source Observable.
This is an alias for
publish().refCount()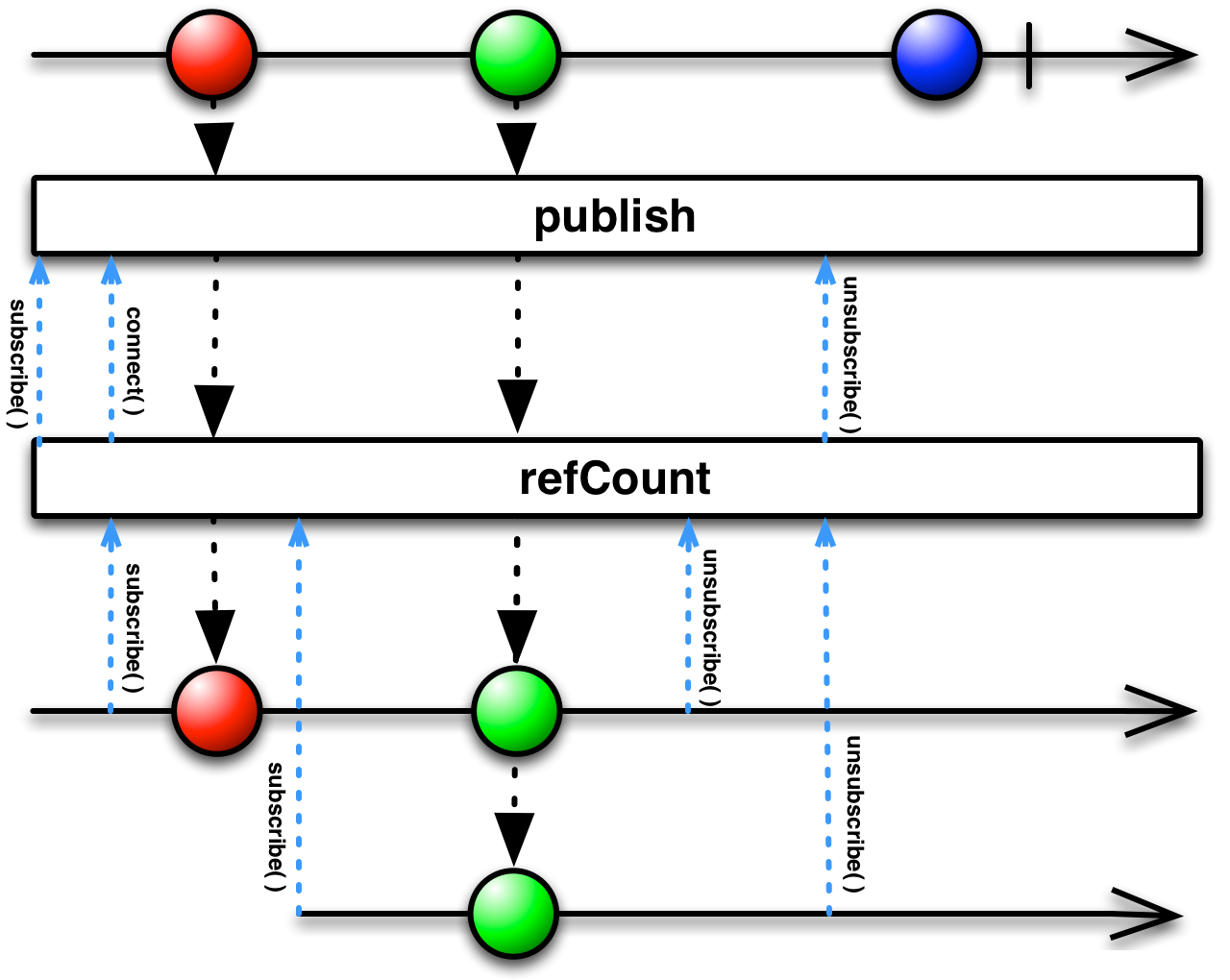
- returns
a Observable that upon connection causes the source Observable to emit items to its rxscalajs.subscription.Subscribers
- Definition Classes
- Observable
- Since
0.19
-
def
single: Observable[T]
If the source Observable completes after emitting a single item, return an Observable that emits that item.
If the source Observable completes after emitting a single item, return an Observable that emits that item. If the source Observable emits more than one item or no items, notify of an
IllegalArgumentExceptionorNoSuchElementExceptionrespectively.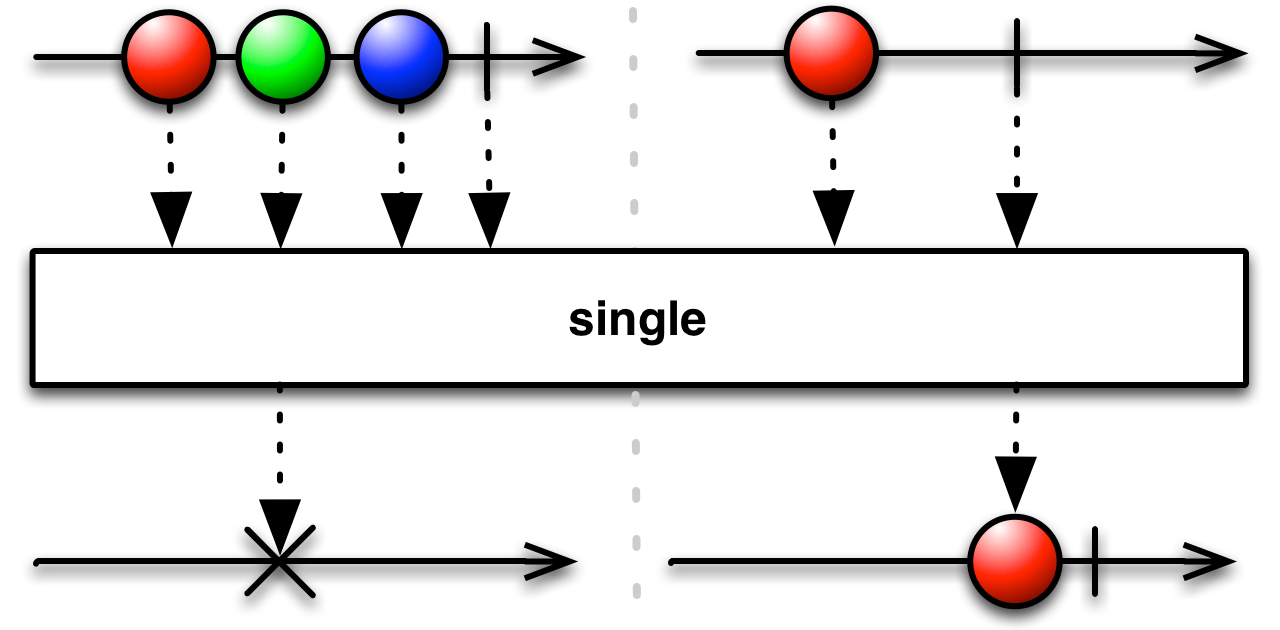
- returns
an Observable that emits the single item emitted by the source Observable
- Definition Classes
- Observable
- See also
"MSDN: Observable.singleAsync()"
-
def
single(predicate: (T, Int, Observable[T]) ⇒ Boolean): Observable[T]
If the source Observable completes after emitting a single item, return an Observable that emits that item.
If the source Observable completes after emitting a single item, return an Observable that emits that item. If the source Observable emits more than one item or no items, notify of an
IllegalArgumentExceptionorNoSuchElementExceptionrespectively.
- returns
an Observable that emits the single item emitted by the source Observable
- Definition Classes
- Observable
- See also
"MSDN: Observable.singleAsync()"
-
def
skip(total: Int): Observable[T]
Returns an Observable that skips the first
numitems emitted by the source Observable and emits the remainder.Returns an Observable that skips the first
numitems emitted by the source Observable and emits the remainder.
- total
the number of items to skip
- returns
an Observable that is identical to the source Observable except that it does not emit the first
numitems that the source emits
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
skipUntil[U](notifier: Observable[U]): Observable[T]
Returns an Observable that skips items emitted by the source Observable until a second Observable emits an item.
Returns an Observable that skips items emitted by the source Observable until a second Observable emits an item.

- notifier
the second Observable that has to emit an item before the source Observable's elements begin to be mirrored by the resulting Observable
- returns
an Observable that skips items from the source Observable until the second Observable emits an item, then emits the remaining items
- Definition Classes
- Observable
- See also
-
def
skipWhile(predicate: (T, Int) ⇒ Boolean): Observable[T]
Returns an Observable that bypasses all items from the source Observable as long as the specified condition holds true.
Returns an Observable that bypasses all items from the source Observable as long as the specified condition holds true. Emits all further source items as soon as the condition becomes false.
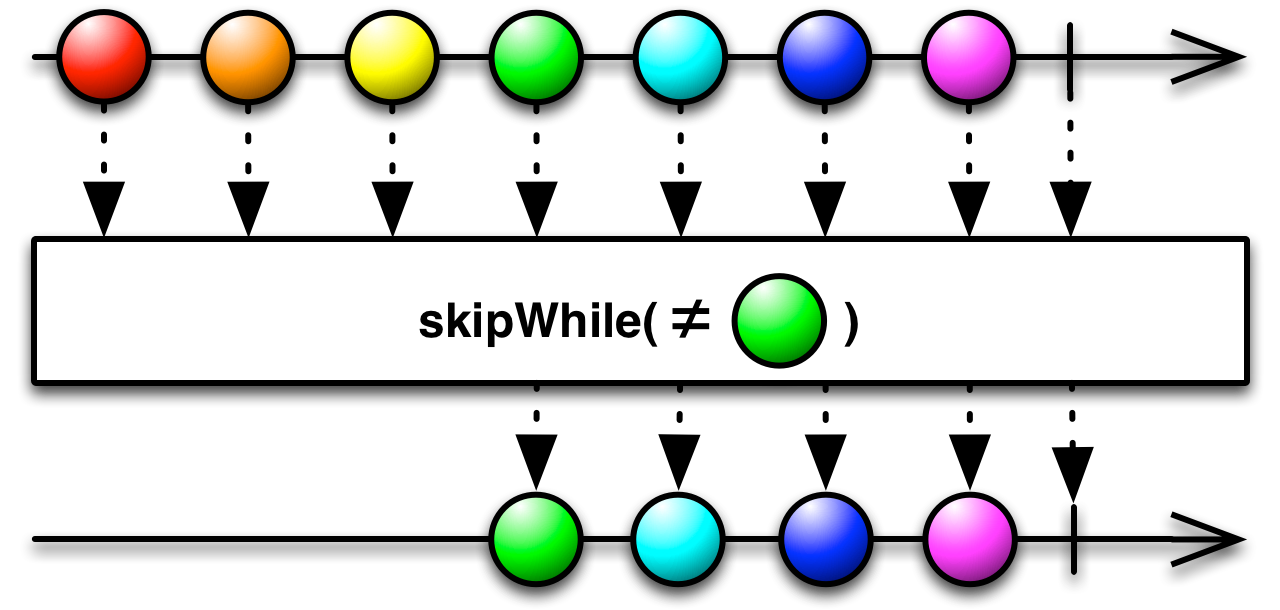
- predicate
A function to test each item emitted from the source Observable for a condition.
- returns
an Observable that emits all items from the source Observable as soon as the condition becomes false.
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
sliding(count: Int, skip: Int): Observable[Observable[T]]
Creates an Observable which produces windows of collected values.
Creates an Observable which produces windows of collected values. This Observable produces windows every
skipvalues, each containingcountelements. When the source Observable completes or encounters an error, the current window is emitted and the event is propagated.- count
The maximum size of each window before it should be emitted.
- skip
How many produced values need to be skipped before starting a new window. Note that when
skipandcountare equal that this is the same operation aswindow(int).- returns
An rxscalajs.Observable which produces windows every
skipvalues containing at mostcountproduced values.
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
startWith[U >: T](elem: U): Observable[U]
Returns an Observable that emits a specified item before it begins to emit items emitted by the source Observable.
Returns an Observable that emits a specified item before it begins to emit items emitted by the source Observable.

- elem
the item to emit
- returns
an Observable that emits the specified item before it begins to emit items emitted by the source Observable
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
startWith[U >: T](elem: U, scheduler: Scheduler): Observable[U]
Returns an Observable that emits a specified item before it begins to emit items emitted by the source Observable.
Returns an Observable that emits a specified item before it begins to emit items emitted by the source Observable.

- elem
the item to emit
- scheduler
The rxscalajs.Scheduler to use internally to manage the timers which handle timeout for each event.
- returns
an Observable that emits the specified item before it begins to emit items emitted by the source Observable
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
startWithMany[U >: T](elements: U*): Observable[U]
Returns an Observable that emits a specified sequence of items before it begins to emit items emitted by the source Observable.
Returns an Observable that emits a specified sequence of items before it begins to emit items emitted by the source Observable.

- elements
the items to emit
- returns
an Observable that emits the specified item before it begins to emit items emitted by the source Observable
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
subscribe(observer: Observer[T]): Subscription
Call this method to subscribe an Observer for receiving items and notifications from the Observable.
Call this method to subscribe an Observer for receiving items and notifications from the Observable.
A typical implementation of
subscribedoes the following:It stores a reference to the Observer in a collection object, such as a
List[T]object.It returns a reference to the subscription.Subscription interface. This enables Observers to unsubscribe, that is, to stop receiving items and notifications before the Observable stops sending them, which also invokes the Observer's Observer.complete() method.
An
Observable[T]instance is responsible for accepting all subscriptions and notifying all Observers. Unless the documentation for a particularObservable[T]implementation indicates otherwise, Observers should make no assumptions about the order in which multiple Observers will receive their notifications.- returns
a subscription.Subscription reference whose
unsubscribemethod can be called to stop receiving items before the Observable has finished sending them
- Definition Classes
- Observable
- See also
-
def
subscribe(onNext: (T) ⇒ Unit, error: (Any) ⇒ Unit = e => (), complete: () ⇒ Unit = () => ()): Subscription
Call this method to subscribe an Observer for receiving items and notifications from the Observable.
Call this method to subscribe an Observer for receiving items and notifications from the Observable.
A typical implementation of
subscribedoes the following:It stores a reference to the Observer in a collection object, such as a
List[T]object.It returns a reference to the subscription.Subscription interface. This enables Observers to unsubscribe, that is, to stop receiving items and notifications before the Observable stops sending them, which also invokes the Observer's complete method.
An
Observable[T]instance is responsible for accepting all subscriptions and notifying all Observers. Unless the documentation for a particularObservable[T]implementation indicates otherwise, Observers should make no assumptions about the order in which multiple Observers will receive their notifications.- returns
a subscription.Subscription reference whose
unsubscribemethod can be called to stop receiving items before the Observable has finished sending them
- Definition Classes
- Observable
- See also
-
def
switch[U]: Observable[U]
[use case] Given an Observable that emits Observables, creates a single Observable that emits the items emitted by the most recently published of those Observables.
[use case]Given an Observable that emits Observables, creates a single Observable that emits the items emitted by the most recently published of those Observables.
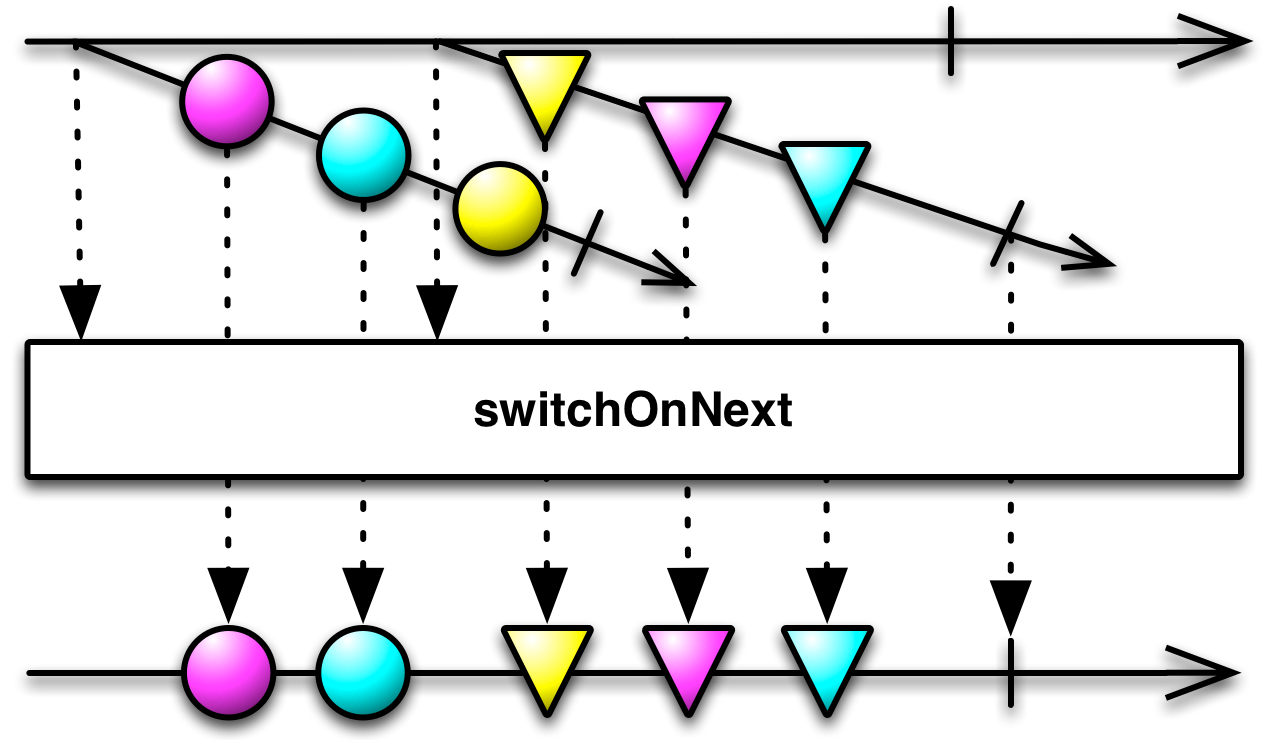
This operation is only available if
thisis of typeObservable[Observable[U]]for someU, otherwise you'll get a compilation error.- returns
an Observable that emits only the items emitted by the most recently published Observable
- Definition Classes
- Observable
Full Signaturedef switch[U](implicit evidence: <:<[Observable[T], Observable[Observable[U]]]): Observable[U]
-
def
switchMap[R](project: (T) ⇒ Observable[R]): Observable[R]
Returns a new Observable by applying a function that you supply to each item emitted by the source Observable that returns an Observable, and then emitting the items emitted by the most recently emitted of these Observables.
Returns a new Observable by applying a function that you supply to each item emitted by the source Observable that returns an Observable, and then emitting the items emitted by the most recently emitted of these Observables.
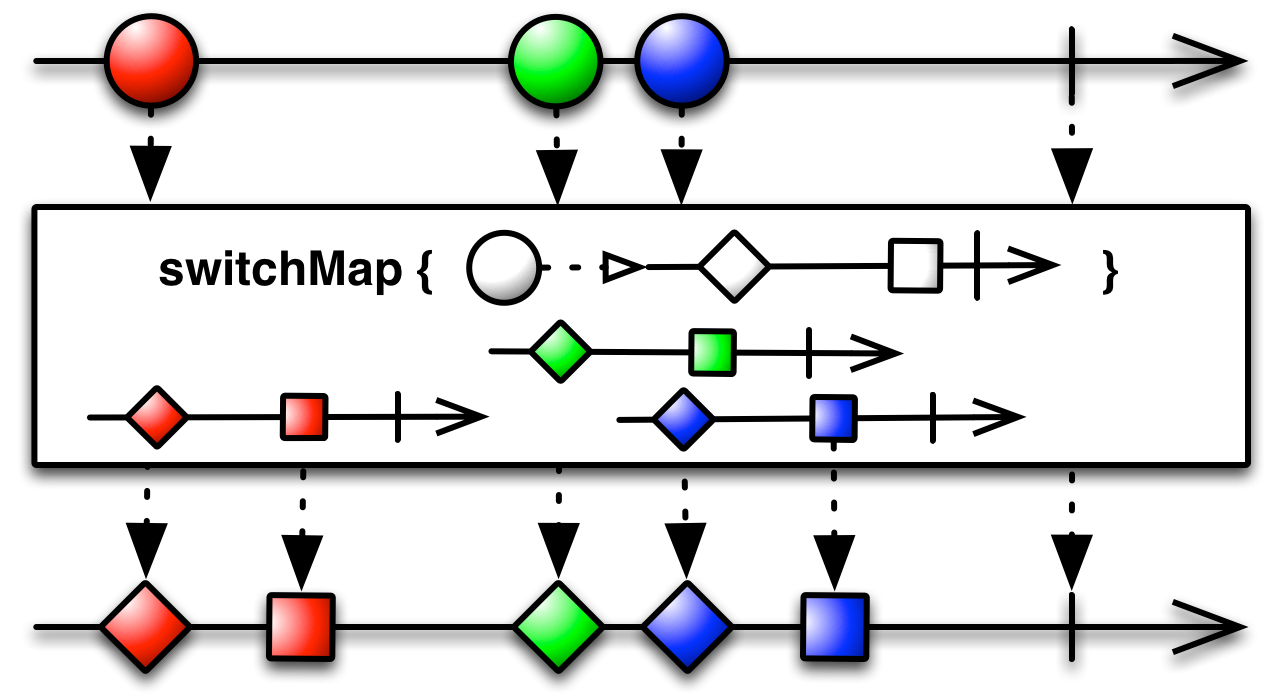
- project
a function that, when applied to an item emitted by the source Observable, returns an Observable
- returns
an Observable that emits the items emitted by the Observable returned from applying a function to the most recently emitted item emitted by the source Observable
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
switchMapTo[R](innerObservable: Observable[R]): Observable[R]
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
final
def
synchronized[T0](arg0: ⇒ T0): T0
- Definition Classes
- AnyRef
-
def
take(total: Int): Observable[T]
Returns an Observable that emits only the first
numitems emitted by the source Observable.Returns an Observable that emits only the first
numitems emitted by the source Observable.
This method returns an Observable that will invoke a subscribing rxscalajs.subscription.ObserverFacade's onNext function a maximum of
numtimes before invoking onCompleted.- total
the number of items to take
- returns
an Observable that emits only the first
numitems from the source Observable, or all of the items from the source Observable if that Observable emits fewer thannumitems
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
takeLast(total: Int): Observable[T]
Returns an Observable that emits only the last
countitems emitted by the source Observable.Returns an Observable that emits only the last
countitems emitted by the source Observable.
- total
the number of items to emit from the end of the sequence emitted by the source Observable
- returns
an Observable that emits only the last
countitems emitted by the source Observable
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
takeUntil[U](notifier: Observable[U]): Observable[T]
Returns an Observable that emits the items from the source Observable only until the
otherObservable emits an item.Returns an Observable that emits the items from the source Observable only until the
otherObservable emits an item.
- notifier
the Observable whose first emitted item will cause
takeUntilto stop emitting items from the source Observable- returns
an Observable that emits the items of the source Observable until such time as
otheremits its first item
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
takeWhile(predicate: (T, Int) ⇒ Boolean): Observable[T]
Returns an Observable that emits items emitted by the source Observable so long as a specified condition is true.
Returns an Observable that emits items emitted by the source Observable so long as a specified condition is true.
- predicate
a function that evaluates an item emitted by the source Observable and returns a Boolean
- returns
an Observable that emits the items from the source Observable so long as each item satisfies the condition defined by
predicate
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
throttle(durationSelector: (T) ⇒ Observable[Int]): Observable[T]
Emits a value from the source Observable, then ignores subsequent source values for a duration determined by another Observable, then repeats this process.
Emits a value from the source Observable, then ignores subsequent source values for a duration determined by another Observable, then repeats this process.
It's like throttleTime, but the silencing duration is determined by a second Observable.

throttleemits the source Observable values on the output Observable when its internal timer is disabled, and ignores source values when the timer is enabled. Initially, the timer is disabled. As soon as the first source value arrives, it is forwarded to the output Observable, and then the timer is enabled by calling thedurationSelectorfunction with the source value, which returns the "duration" Observable. When the duration Observable emits a value or completes, the timer is disabled, and this process repeats for the next source value.- durationSelector
A function that receives a value from the source Observable, for computing the silencing duration for each source value, returned as an Observable or a Promise.
- returns
An Observable that performs the throttle operation to limit the rate of emissions from the source.
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
throttleTime(delay: Int): Observable[T]
Debounces by dropping all values that are followed by newer values before the timeout value expires.
Debounces by dropping all values that are followed by newer values before the timeout value expires. The timer resets on each
onNextcall.NOTE: If events keep firing faster than the timeout then no data will be emitted.
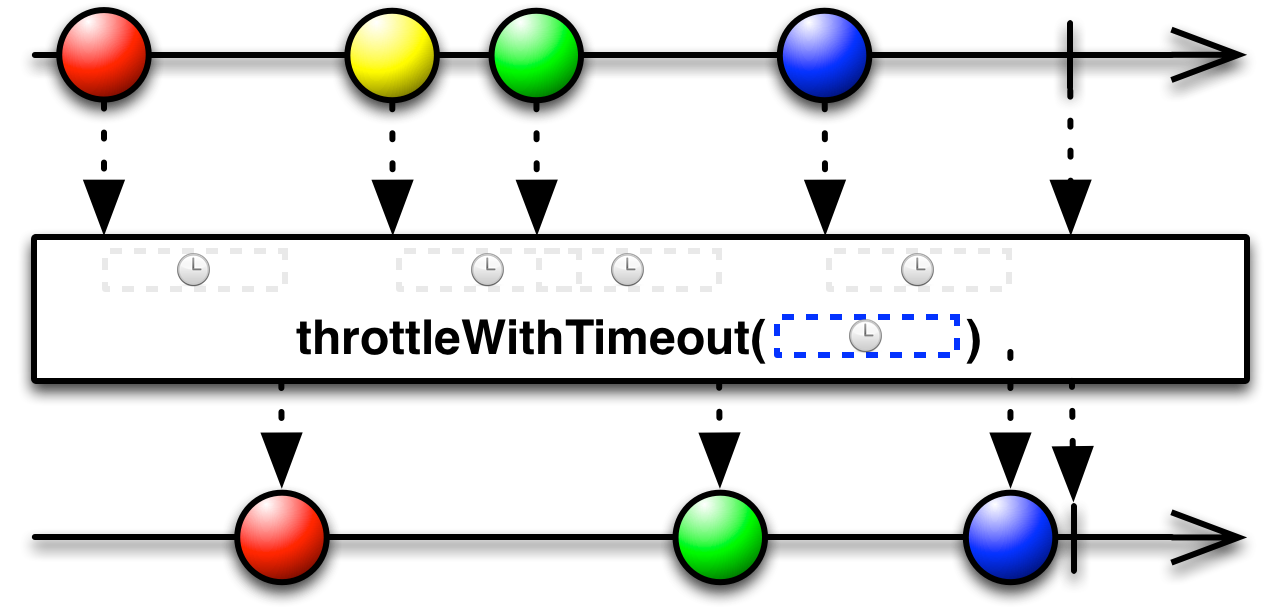
- delay
The time each value has to be 'the most recent' of the rxscalajs.Observable to ensure that it's not dropped.
- returns
Observable which performs the throttle operation.
- Definition Classes
- Observable
- See also
Observable.debounce
-
def
throttleTime(delay: FiniteDuration): Observable[T]
Debounces by dropping all values that are followed by newer values before the timeout value expires.
Debounces by dropping all values that are followed by newer values before the timeout value expires. The timer resets on each
onNextcall.NOTE: If events keep firing faster than the timeout then no data will be emitted.

- delay
The time each value has to be 'the most recent' of the rxscalajs.Observable to ensure that it's not dropped.
- returns
Observable which performs the throttle operation.
- Definition Classes
- Observable
- See also
Observable.debounce
-
def
throttleTime(delay: FiniteDuration, scheduler: Scheduler): Observable[T]
Debounces by dropping all values that are followed by newer values before the timeout value expires.
Debounces by dropping all values that are followed by newer values before the timeout value expires. The timer resets on each
onNextcall.NOTE: If events keep firing faster than the timeout then no data will be emitted.

- delay
The time each value has to be 'the most recent' of the rxscalajs.Observable to ensure that it's not dropped.
- scheduler
The rxscalajs.Scheduler to use internally to manage the timers which handle timeout for each event.
- returns
Observable which performs the throttle operation.
- Definition Classes
- Observable
- See also
Observable.debounce
-
def
timeInterval: Observable[TimeInterval[T]]
Returns an Observable that emits records of the time interval between consecutive items emitted by the source Observable.
Returns an Observable that emits records of the time interval between consecutive items emitted by the source Observable.
- returns
an Observable that emits time interval information items
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
timeout(due: Int): Observable[T]
Applies a timeout policy for each item emitted by the Observable, using the specified scheduler to run timeout timers.
Applies a timeout policy for each item emitted by the Observable, using the specified scheduler to run timeout timers. If the next item isn't observed within the specified timeout duration starting from its predecessor, a specified fallback Observable sequence produces future items and notifications from that point on.
- due
maximum duration between items before a timeout occurs
- returns
the source Observable modified so that it will switch to the fallback Observable in case of a timeout
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
timeout[U](due: Int, scheduler: Scheduler): Observable[T]
Applies a timeout policy for each item emitted by the Observable, using the specified scheduler to run timeout timers.
Applies a timeout policy for each item emitted by the Observable, using the specified scheduler to run timeout timers. If the next item isn't observed within the specified timeout duration starting from its predecessor, a specified fallback Observable sequence produces future items and notifications from that point on.

- due
maximum duration between items before a timeout occurs
- scheduler
Scheduler to run the timeout timers on
- returns
the source Observable modified so that it will switch to the fallback Observable in case of a timeout
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
timeoutWith[R](due: Int, withObservable: Observable[R]): Observable[R]
Applies a timeout policy for each item emitted by the Observable, using the specified scheduler to run timeout timers.
Applies a timeout policy for each item emitted by the Observable, using the specified scheduler to run timeout timers. If the next item isn't observed within the specified timeout duration starting from its predecessor, a specified fallback Observable produces future items and notifications from that point on.
- due
maximum duration between items before a timeout occurs
- withObservable
fallback Observable to use in case of a timeout
- returns
the source Observable modified to switch to the fallback Observable in case of a timeout
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
timestamp: Observable[Timestamp[T]]
Wraps each item emitted by a source Observable in a timestamped tuple.
Wraps each item emitted by a source Observable in a timestamped tuple.
- returns
an Observable that emits timestamped items from the source Observable
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
implicit
def
toFacade[A](observable: Observable[A]): ObservableFacade[A]
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
toSeq: Observable[Seq[T]]
Returns an Observable that emits a single item, a list composed of all the items emitted by the source Observable.
Returns an Observable that emits a single item, a list composed of all the items emitted by the source Observable.
Normally, an Observable that returns multiple items will do so by invoking its rxscalajs.subscription.ObserverFacade's onNext method for each such item. You can change this behavior, instructing the Observable to compose a list of all of these items and then to invoke the Observer's
onNextfunction once, passing it the entire list, by calling the Observable'stoListmethod prior to calling itsObservable.subscribemethod.Be careful not to use this operator on Observables that emit infinite or very large numbers of items, as you do not have the option to unsubscribe.
- returns
an Observable that emits a single item: a List containing all of the items emitted by the source Observable.
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
toString(): String
- Definition Classes
- AnyRef → Any
-
def
tumbling[I](boundaries: Observable[I]): Observable[Observable[T]]
Creates an Observable which produces windows of collected values.
Creates an Observable which produces windows of collected values. This Observable produces connected non-overlapping windows. The boundary of each window is determined by the items emitted from a specified boundary-governing Observable.
- boundaries
an Observable whose emitted items close and open windows. Note: This is a by-name parameter, so it is only evaluated when someone subscribes to the returned Observable.
- returns
An Observable which produces connected non-overlapping windows. The boundary of each window is determined by the items emitted from a specified boundary-governing Observable.
- Definition Classes
- Observable
- def unsubscribe(): Unit
-
final
def
wait(): Unit
- Definition Classes
- AnyRef
- Annotations
- @throws( ... )
-
final
def
wait(arg0: Long, arg1: Int): Unit
- Definition Classes
- AnyRef
- Annotations
- @throws( ... )
-
final
def
wait(arg0: Long): Unit
- Definition Classes
- AnyRef
- Annotations
- @throws( ... )
-
def
window[I](windowBoundaries: Observable[I]): Observable[Observable[T]]
Creates an Observable which produces windows of collected values.
Creates an Observable which produces windows of collected values. This Observable produces connected non-overlapping windows. The boundary of each window is determined by the items emitted from a specified boundary-governing Observable.

- windowBoundaries
an Observable whose emitted items close and open windows. Note: This is a by-name parameter, so it is only evaluated when someone subscribes to the returned Observable.
- returns
An Observable which produces connected non-overlapping windows. The boundary of each window is determined by the items emitted from a specified boundary-governing Observable.
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
windowCount(windowSize: Int, startWindowEvery: Int = 0): Observable[Observable[T]]
Creates an Observable which produces windows of collected values.
Creates an Observable which produces windows of collected values. This Observable produces windows every
skipvalues, each containingcountelements. When the source Observable completes or encounters an error, the current window is emitted and the event is propagated.- windowSize
The maximum size of each window before it should be emitted.
- startWindowEvery
How many produced values need to be skipped before starting a new window. Note that when
skipandcountare equal that this is the same operation aswindow(int).- returns
An rxscalajs.Observable which produces windows every
skipvalues containing at mostcountproduced values.
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
windowTime(timespan: FiniteDuration): Observable[Observable[T]]
Creates an Observable which produces windows of collected values.
Creates an Observable which produces windows of collected values. This Observable produces connected non-overlapping windows, each of a fixed duration specified by the
timespanargument or a maximum size specified by thecountargument (which ever is reached first). When the source Observable completes or encounters an error, the current window is emitted and the event is propagated.- timespan
The period of time each window is collecting values before it should be emitted, and replaced with a new window.
- returns
An rxscalajs.Observable which produces connected non-overlapping windows which are emitted after a fixed duration or when the window has reached maximum capacity (which ever occurs first).
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
windowTime(timespan: FiniteDuration, scheduler: Scheduler): Observable[Observable[T]]
Creates an Observable which produces windows of collected values.
Creates an Observable which produces windows of collected values. This Observable produces connected non-overlapping windows, each of a fixed duration specified by the
timespanargument or a maximum size specified by thecountargument (which ever is reached first). When the source Observable completes or encounters an error, the current window is emitted and the event is propagated.- timespan
The period of time each window is collecting values before it should be emitted, and replaced with a new window.
- scheduler
The rxscalajs.Scheduler to use when determining the end and start of a window.
- returns
An rxscalajs.Observable which produces connected non-overlapping windows which are emitted after a fixed duration or when the window has reached maximum capacity (which ever occurs first).
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
windowTime(timespan: Int, timeshift: Int): Observable[Observable[T]]
Creates an Observable which produces windows of collected values.
Creates an Observable which produces windows of collected values. This Observable produces connected non-overlapping windows, each of a fixed duration specified by the
timespanargument or a maximum size specified by thecountargument (which ever is reached first). When the source Observable completes or encounters an error, the current window is emitted and the event is propagated.- timespan
The period of time each window is collecting values before it should be emitted, and replaced with a new window.
- timeshift
the period of time after which a new window will be created
- returns
An rxscalajs.Observable which produces connected non-overlapping windows which are emitted after a fixed duration or when the window has reached maximum capacity (which ever occurs first).
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
windowTime(timespan: FiniteDuration, timeshift: FiniteDuration): Observable[Observable[T]]
Creates an Observable which produces windows of collected values.
Creates an Observable which produces windows of collected values. This Observable produces connected non-overlapping windows, each of a fixed duration specified by the
timespanargument or a maximum size specified by thecountargument (which ever is reached first). When the source Observable completes or encounters an error, the current window is emitted and the event is propagated.- timespan
The period of time each window is collecting values before it should be emitted, and replaced with a new window.
- timeshift
the period of time after which a new window will be created
- returns
An rxscalajs.Observable which produces connected non-overlapping windows which are emitted after a fixed duration or when the window has reached maximum capacity (which ever occurs first).
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
windowTime(timespan: FiniteDuration, timeshift: FiniteDuration, scheduler: Scheduler): Observable[Observable[T]]
Creates an Observable which produces windows of collected values.
Creates an Observable which produces windows of collected values. This Observable produces connected non-overlapping windows, each of a fixed duration specified by the
timespanargument or a maximum size specified by thecountargument (which ever is reached first). When the source Observable completes or encounters an error, the current window is emitted and the event is propagated.- timespan
The period of time each window is collecting values before it should be emitted, and replaced with a new window.
- timeshift
the period of time after which a new window will be created
- scheduler
The rxscalajs.Scheduler to use when determining the end and start of a window.
- returns
An rxscalajs.Observable which produces connected non-overlapping windows which are emitted after a fixed duration or when the window has reached maximum capacity (which ever occurs first).
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
windowToggle[U, O](openings: Observable[O])(closingSelector: (O) ⇒ Observable[U]): Observable[Observable[T]]
Creates an Observable which produces windows of collected values.
Creates an Observable which produces windows of collected values. Chunks are created when the specified
openingsObservable produces an object. That object is used to construct an Observable to emit windows, feeding it intoclosingsfunction. Windows are emitted when the created Observable produces an object.- openings
The rxscalajs.Observable which when it produces an object, will cause another window to be created.
- closingSelector
The function which is used to produce an rxscalajs.Observable for every window created. When this rxscalajs.Observable produces an object, the associated window is emitted.
- returns
An rxscalajs.Observable which produces windows which are created and emitted when the specified rxscalajs.Observables publish certain objects.
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
windowWhen[U](closingSelector: () ⇒ Observable[U]): Observable[Observable[T]]
Creates an Observable which produces windows of collected values.
Creates an Observable which produces windows of collected values. This Observable produces connected non-overlapping windows. The boundary of each window is determined by the items emitted from a specified boundary-governing Observable.

- closingSelector
an Observable whose emitted items close and open windows. Note: This is a by-name parameter, so it is only evaluated when someone subscribes to the returned Observable.
- returns
An Observable which produces connected non-overlapping windows. The boundary of each window is determined by the items emitted from a specified boundary-governing Observable.
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
withFilter(p: (T) ⇒ Boolean): WithFilter[T]
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
withLatestFrom[U](other: Observable[U]): Observable[(T, U)]
Merges the specified Observable into this Observable sequence by using the
resultSelectorfunction only when the source Observable (this instance) emits an item.Merges the specified Observable into this Observable sequence by using the
resultSelectorfunction only when the source Observable (this instance) emits an item.
- other
the other Observable
- returns
an Observable that merges the specified Observable into this Observable by combining the elements into a tuple only when the source Observable sequence (this instance) emits an item
- Definition Classes
- Observable
- Since
(if this graduates from Experimental/Beta to supported, replace this parenthetical with the release number)
- See also
-
def
withLatestFromWith[U, R](other: Observable[U])(project: (T, U) ⇒ R): Observable[R]
Merges the specified Observable into this Observable sequence by using the
resultSelectorfunction only when the source Observable (this instance) emits an item.Merges the specified Observable into this Observable sequence by using the
resultSelectorfunction only when the source Observable (this instance) emits an item.
- other
the other Observable
- project
the function to call when this Observable emits an item and the other Observable has already emitted an item, to generate the item to be emitted by the resulting Observable
- returns
an Observable that merges the specified Observable into this Observable by using the
resultSelectorfunction only when the source Observable sequence (this instance) emits an item
- Definition Classes
- Observable
- Since
(if this graduates from Experimental/Beta to supported, replace this parenthetical with the release number)
- See also
-
def
zip[U](that: Observable[U]): Observable[(T, U)]
Returns an Observable formed from this Observable and another Observable by combining corresponding elements in pairs.
Returns an Observable formed from this Observable and another Observable by combining corresponding elements in pairs. The number of
onNextinvocations of the resultingObservable[(T, U)]is the minumum of the number ofonNextinvocations ofthisandthat.- that
the Observable to zip with
- returns
an Observable that pairs up values from
thisandthatObservables.
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
zipWith[U, R](that: Observable[U])(project: (T, U) ⇒ R): Observable[R]
Returns an Observable that emits items that are the result of applying a specified function to pairs of values, one each from the source Observable and a specified Iterable sequence.
Returns an Observable that emits items that are the result of applying a specified function to pairs of values, one each from the source Observable and a specified Iterable sequence.
Note that the
otherIterable is evaluated as items are observed from the source Observable it is not pre-consumed. This allows you to zip infinite streams on either side.- that
the Iterable sequence
- project
a function that combines the pairs of items from the Observable and the Iterable to generate the items to be emitted by the resulting Observable
- returns
an Observable that pairs up values from the source Observable and the
otherIterable sequence and emits the results ofselectorapplied to these pairs
- Definition Classes
- Observable
-
def
zipWithIndex: Observable[(T, Int)]
Zips this Observable with its indices.
Zips this Observable with its indices.
- returns
An Observable emitting pairs consisting of all elements of this Observable paired with their index. Indices start at 0.
- Definition Classes
- Observable